| Week 1 | T&L Activities: Initial Assesment: www.Socrative.com Introduction to unit
Discuss how the website they will complete will be used in their digital portfolio (Unit 3: A Digital Portfolio), and how they should document the process of developing their website for inclusion in their portfolio.
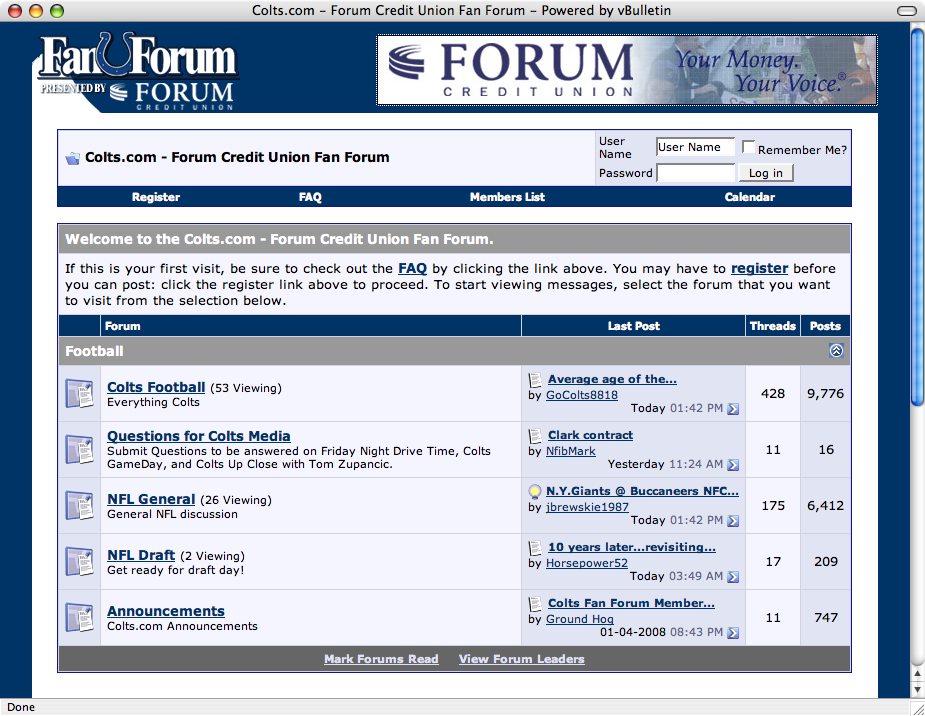
Typical uses of websitesAs you probably know there are millions and millions of websites on the internet today, each different from each other, offering services, business tools, personal and entertainment. Some of the most common purposes of websites are covered below. Presenting information
Websites are used by businesses and by people for the purposes of both for presenting information, such as news, and in business situations products and or services and advertising these online. Nowadays almost all companies have their own website. Some of the best known news websites are used today are BBC News (www.bbc.co.uk). Storing information
Websites can provide services that enable you to save information and data to them this is commonly referred to as the 'cloud', this is a relatively recent development in information and data storage. This service uses the internet and the webservers to store information rather than using local storage such as your computer's C:/ disk drive or other memory sticks. Browsing and searching for information
Search engines and the use of a specific engine has change most of our lives. The internet search engine Google has become the worlds leading search engine leading to the verb.‘to Google’ to be included in to the Oxford English Dictionary. Most people that you come across nowadays will suggest that you ‘Google it’ if you do not know the answer. Improving productivity
The web has enabled an alternative way of communication, Email. The use of Email has completely changed the way that people and business communicate, it has enabled people and companies to share information and data, send electronic documents to each other almost instantly. The use of video conferencing has allowed people and companies to have meetings and to see things irrelevant of location and time. This has helped companies and people to save money in not requiring them to spend time in travelling. Making decisionsOver the past 10 years there have been more sites that enable us to make better decisions on products and services as they provide us with information from a number of different places in one place. Example of these sorts of sites are Go compare, moneysaving expert and compare the market, all these sites offer people all the information that can be found to allow them to make a decision on which product or service suits their needs and for the best price. Make a list of all the websites you visit in a week and classify each of them using the list above. What type has the most number of websites from your list? Which individual sites do you visit most often? What are the features of your favourite sites that attract you to them? Communication with peopleYou will probably be one of the meny millions that use social networking sites that are available today, these include Facebook, Myspace, Mebo, Bebo and the list grows longer. People use these sites as ways to communicate with their friends but to also get an look in to what they are doing, going to do, or have done. These sites now offer the ability for users to chat with friends though an instant messenger type interface. There are lots of other instant messenger services that are available to users, such as Yahoo Chat and MSN, these are popular and some include video chatting as well as text chat such as Skype. Media sharingAn area of the internet has evolved is the ability to listen to music or live radio, and how we watch films. Companies like Apple offer services like iTunes that enable users to purchase and download music through the web, whilst other sites like YouTube allow people to view and share videos on the internet covering a wide range of areas. Radio stations are now broadcasting in digital as well as conventional analogue, so you can now listen to your favourite stations and DJ’s over the internet, there are some radio stations that only broadcast digitally like BBC, Radio 6 Music. E-commerceThe use of the internet to all us to do our shopping has dramatically increase over a number of years. Companies like John Lewis and PC world have all embraced this way of doing some of its business. As well as these large company’s there are others that are online-only the like Amazon and Ebuyer. A large amount of business is now done online. EducationThe internet holds huge amount of resources and information on pretty much every subject That you can think of. If you wanted to, you could find information about the number of people that have walked on the moon by using a simple search on the internet. Some sites are specialist and offer detailed information to its users and some are general and give the basic facts, however all this information is available to you, and in the most part it is FREE. An example of such sites is www.tomshardware.co.uk, which provides information about PC hardware, it also provides details on training courses and contains video instructions on how to do all sorts of practical things. Downloading informationOn the internet today there are a number of websites enable you to download digital content for you use as you wish. A well-known example is iTunes where you can buy and download music, videos and now ringtones. There are other sites that allow you to download their software products directly from their website. A example of this is Microsoft, where you are able to download the latest version of a web browser. You must be careful when downloading any files from any sites and some sites are out there that are bad, these are sites that use Phishing to get your information, and others that allow you to download viruses that can attack your computer and the files on it, and can even send your private information to bad people from your computer. The information covered in this page covers the knowledge and understanding linked to the criterion in the table below. Learners to identify website features that appeal to different types of audiences based on categories provided by the teacher. Concluding discussion: Why businesses/individuals want websites created for them, how to attract people to a website and why it is important to.
Website ProductionWelcome to unit 13, this unit is all about the wonderful world of web design. This unit will take you through the key stages to create a website and the required planning and testing that is required to enable the creation of a sucsessful web project.
Files that support this week | English:
Search for information, using different sources, and multiple search criteria in at least one case. Review and Analysis of information and features. 0 |
Assessment:
Clarifying Learning Objectives - Using coloured discs and/or peer explanation, check to ensure that learners have understood the learning objectives. 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
LOA Understand the uses and features of websites |
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
1A.1 Identify the intended use and features of two websites. 2A.P1 Explain the intended uses and features of two different websites 2A.M1 Review how the features in two websites improve presentation, usability, accessibility and performance 2A.D1 Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the websites |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Analysis of information: Interpreting Results, Drawing conclusions from data, Comparing data Using Numbers: Counting, Place value, adding and subtracting, multiplying and dividing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
Case Study: Junior web developer I wanted to work in web development, as I think it is one of the fastest developing and most exciting areas in IT. I learned about the basics of web development when I studied for my BTEC First course and then I went on to study it in more detail at college and university. After I left university I applied for a lot of jobs with no luck. After about three months, I found work at a local company which makes fashion wear. They were looking for a junior web developer to update their website and I got the job. Their website changes all the time, with new ranges of clothing coming out and old ones needing to be removed. So far, I am happy with the job. Some parts of it are quite tedious, like uploading the new files, but I am learning new things all the time, and as I learn how to do more, I can get involved in the more interesting and exciting projects. We are currently looking at creating a version of our website for mobile users, which I am looking forward to working on. Questions
|
E&D / BV
Mutual Respect Rule of Law |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 2 | T&L Activities:Features of Websites.All websites have features in them, these are categorised as
Lets look in to these category's a little closer.
Hyper-linksWhat are hyper-links? these are the nuts and bolts that hold the internet as we know it together! Hyper-links connect web-pages together, just like this one! when you come across a button, snippet of text or an image that when you click on it, it takes you to another page, file, or location then this is a hyper-link. Normally in a raw unformatted style these will look like the image below.
action buttonsButtons use the hyper-link feature to enable them to work, buttons allow users to quickly see that something can be done, or happen if it is pressed. Buttons can be styled in many different ways to make them look nice on a website, or to make them match the theme that the website has.
hot spotsHot spots are great ways to cut an image into different links to different pages, take for instance the picture of the UK, this one image can be divided up into a number of regions, cities, towns e.t.c. so when a user clicks on that area of the image they are taken to that locations pages or information.
templatesWhy create it from scratch if you can use a pre-created template. Templates are useful, they give us the ability to create something quickly, and to a standard or theme. These can be created by you and used over and over again, think of this website, it has a similar layout and visual style, so I use an empty template page that I update the content inside to discuss and provide activities for your to read, learn and understand. I also add links to other sites and images that I feel could be of use to you too.
email linksOn some pages on most sites there will be a link/email address that the owner has put there for you to contact them for advice, their products, investment amongst many other reasons. It is a good idea to include one on a website as this could provide business opportunities.
registration and loginsSome websites have databases and private areas that only member's can get to, in order to gain access to these the user will need to login, these logins are normally found in the top right hand side of the website, however this is not the only place that they can appear.
forms (user input and feedback)
accessibility, e.g. text to speech.
e-commerce facilities
online forums
aesthetics, e.g. colours, layout, graphics/video/animation, audio, text, styles (use of style sheets).
Files that support this week | English:
Review and Analysis of information and features. 0 |
Assessment:
Peer Assessment of Independent Work - Learners work in groups to assess each other's work and make recommendations for improvement. 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
Learning aim A: Understand the uses and features of websites
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
1A.1 Identify the intended use and features of two websites. 2A.P1 Explain the intended uses and features of two different websites. 2A.M1 Review how the features in two websites improve presentation. usability, accessibility, and performance 2A.D1 Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the websites. 1B.2 Identify the purpose and user requirements of the website. 1B.3 Produce a design for a four-page interlinked website, with guidance, including an outline of the proposed solution. 2B.P2 Describe the purpose and user requirements of the website. 2B.P3 Produce a detailed design for an eight-page interlinked website, including; A proposed solution, A list of assets, A test plan 2B.M2 Produce a detailed design for a website, including; Alternative solutions aesthetic feature interactive components 2A.D2 Justify the final design decisions, including; how the design will fulfill the purpose and requirements including any design constraints 1C.4 Prepare assets and content for the website, with guidance. 1C.5 Develop a web site containing four interlinked web pages. with guidance 1C.6 Test the website for functionality and purpose repairing any faults and documenting changes. with guidance. 2C.P5 Develop a web site containing at least eight interlinked web pages. demonstrating awareness of purpose. 2C.P6 Test the website for functionality and purpose, repairing any faults, and documenting changes 2C.M3 Prepare assets and content to the website demonstrating awareness of the users· requirements. with all sources fully referenced. 2C.M5 Test interactivity and gather feedback from others on the'. quality of the website. and use it to improve the website. showing awareness of user requirements. 2C.D3 Refine the website. to improve accessibility and performance. taking account of user feedback and test results. 1D.7 Identify how the final website is suitable for the intended purpose. 2D.P7 Explain how the final website is suitable for the intended audience and purpose. 2D.M7 Review the extent to which the finished website meets the needs of purpose and user requirements. while considering feedback from others and constraints 2D.D4 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Analysis of information: Interpreting Results, Drawing conclusions from data, Comparing data |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV
qwd ddd |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT
gg |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 3 | T&L Activities: Assesment Time - We will now go through the assignment brief to ensure that you understand what is expected and required of you.
Applying styleWhen creating webpage's and websites, the visual style is something that can make or break whether a user stays on the site or navigates away. We know from our research before sites like Lings Car's, can overwhelm users and can distract users away from content.
Types of Website & Improving User ExperianceTypes of websites:
StaticStatic websites are a collection of web pages primarily coded in HyperText Markup Language (HTML). These types of websites present static information to their audience, e.g. a brochure. In the initial early days of the internet, websites were only text these sites remained the same and were only changed when a user downloaded and then re-uploaded the files with the required improvements. DynamicA dynamic website is a collection of web pages that often changes or customises itself frequently and automatically.
Discuss how can user experience of websites be improved with interactivity? In groups of no large than 3 create a list of dynamic and static websites (minimum of 5 for each), review these for there intended aim, target audience and purpose and finally explain what your thoughts on these sites are, in terms of visual appearance and functionality.
Different features of websites can improve the user experience for an individual, business or organisation, e.g.:
Files that support this week | English:
0 |
Assessment:
One-Minute Verbal Assessment - The teacher asks learners to prepare and deliver a one minute verbal summary of a forthcoming or completed activity, session or topic. 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
1A.1 Identify the intended use and features of two websites. 2A.P1 Explain the intended uses and features of two different websites. 2A.M1 Review how the features in two websites improve presentation. usability, accessibility, and performance 2A.D1 Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the websites. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Analysis of information: Interpreting Results, Drawing conclusions from data, Comparing data |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 4 | T&L Activities:Purposes and uses of WebsitesPurposeWhen creating, using and developing a website you must try to understand the purpose of them. In your course, you will be given a scenario or setting to which you must make a submission to. It is vital that you understand who the audience of the site is as this can, and will lead to either success or failure. When creating a site for a client that you will get paid for, who is the audience? Consider the fact that an explanation can be interpreted in many ways, however when planning to create a product, in our case a website, we need to demonstrate that we understand what we are doing and for whom. The best way for us to demonstrate this is by writing down what our understanding is of our project before we even start to think about designing it. It is therefore very important that this is documented from the beginning of our project. User Requirements Now that you understand some part of the purpose of the site and intended target audiences it is time to look at the user's requirements, this could be a list of elements that they would like to see in a website, it could also include the features that they would like to have too. Examples of the types of requirements that a client could require would be things like;
The list above is only an example and not likely to be required in your assessments, however, this concept of a list should be identified and acknowledged when writing about the user's requirements in any document so that your client (your tutor) is aware that you know what you need to include in your site. What type of language would you use in a portfolio website? Word of the Day, use the QR code in the class to find out. Whats its Scrabble score? What types of features would you expect to appeal to a target audience of web users that are close to your age? What features would you select to appeal to different genders? Why would different genders have different features? Would this affect the overall appearance of the site?
Design DocumentationThe process of creating a website or the vision of a website begins at the design stage, you will have at this point been given the details of the users requirements and the target audience, with all of this detail now at your disposal you can produce your vision of the site through the use of, Storyboards, Timelines, Hierarchy diagrams, assets lists and a purposed test plan. These documents are a key piece of evidence that once created will provide a set of guidance documentation that will keep the final development of the site on track. Let's look closer at these documents and their unique importance.
StoryboardsClose your eye's, and clear your mind, You are standing in a field, in front of you are some mountains, at the foot of these are some animals under a tree. Discuss as a group what your vision was. Possibly one of the most key documents that have the ability to save time, a well-created storyboard can provide the detail and information to how a site should look and feel. The more detail the better, in the web development sector this stage can be done by a person that is in another country and the developer will be given these drawings and be expected to create the site from them. create a storyboard of a website that you visit DO NOT INCLUDE THE TITLE/NAME OF THE SITE IN YOUR DESIGN, try to create this without loading it up on your screen, share this with another person in your class, see if they are able to tell you what site that they have chosen. Now that you have swapped your storyboards with others in the group, identify the areas that they could have improved on thier storyboard to make it more clear as to the site that they choose. Storyboards should be supported with some text to enable further understanding, such as the links to content or the overall intended feel and direction of the page. The example below demonstrates the simplest version of a storyboard. A further example of a detailed storyboard. Some storyboards are taken further by creating a mockup, these are photoshop or image editor graphics that are constructed to make an example of how the web page may actually look on a web browser.
Assets ListThe creation of a website may require you to include key images, links to videos or files, the logging of this is therefore important and vital. However at the beginning of the project, your client may already have some of these for you, this could be things like logos and examples of work. This needs to be logged and included in an asset table for a number of reasons.
So what should your assets table look like?
The examples in the table above demonstrate that you understand the name of the file, what kind of file type it is, where the file came from, your intentions with the file, the size of the file and finally whether the file is copyrighted so may need permission to use it. File Types File types that could be used are;
File Sizes and Compression Remember that each of the above file types has different purposes and benefits and you should consider when and where you will use them. Things that can affect users and websites are the sizes of the files, for example, a tif image is not a compressed file this means that it is likely to be large, which could affect the loading time of a web page. Whereas a jpg is a compressed file format and this would be a better option for a graphical file type to use for a web page. TimelinesTo have a plan is to be organised! So with almost all projects, it is key to set out a plan of action in how you intend on completing the project. Each project will have a set of tasks that may happen at set points in time, or, that may need to be completed by a set time. Let's use an example of building a house. Can you put the roof on before the walls have been built? No! so we have a logical order that must be followed and this is the same with creating a website. We can set this out from the beginning, the below is an example of a simple timeline/plan.
Create a timeline template, add to it a plan on how you will prepare for christmas, consider research time, shopping and setting up your christmas tree. HierarchyThe understanding of the flow of the pages is important, we can draw how we would like the pages to link to each other very simply, the image below outlines this. Files that support this week | English:
0 0 |
Assessment:
Learning Capture - Teachers allocate time at the end of the session for the group to write down what they think they have learned. The information shared helps the teacher to see which content he may need to revisit and so shapes future planning. Traffic Lights - Learners use green, amber and red traffic lights to indicate levels of understanding and to attract support from peers and the teacher. 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 5 | T&L Activities:Target Audience and Purpose
The design of your the user interface should reflect the intended target audience. The portfolios appearance and navigation will give an impression on your audience, anyone who will look at your portfolio could be potential employers in an organisation that you are applying to. Anyone looking at the portfolio could be looking for different things, such as, your ability to communicate, your understanding of technical skills During the design, you will need to produce a short paragraph describing the purpose of the portfolio. This will help you identify its purpose. Make sure your paragraphs provide information to the following :
Try creating a project plan using online cloud services such as projectplan365What do you think are the stages of creating a website? spend 10 minutes working in pairs of 2, and identify what you feel are the important stages.
Fill in the blanks by dragging the missing answer.
All Answers Answered Answers Remain
DIGITAL ASSETSOnce the design of a site has happened consideration turns to the files and assets that you will be required to be on, and available to the site for potential visitors. It is essential to consider a number of things in this topic area, these are,
these points can affect the operation and load times of the pages on the portfolio. An example of an asset table.
SOUNDAs has been discussed in the section above our asset can affect the load times of our site, we have reviewed images but what about audio? Some sites have audio that plays on them (this is not advised) but these sounds will need to be loaded much like the images. Again like the images the sounds can be large and the quality can and will effect their loading, so in this case, we use different sound file types that use CODEC's (COmpression DECompression) to reduce the size without noticable quality changes.
See the Pen Simple HTML Page layout - BTEC Level 2 - Unit 13 Web Production by james farrington (@jamesfarrington) on CodePen.
Create a table that you could enter in the assets that you would intend on using in your website project, once you have created this swap your tables with another person in your class and try to complete them. Record any feedback you have about the table in the document, try to suggest improvements and refinements that could make the table, easier to use and understand.
Hierarchy Table/Chart
The use of hierarchy charts/tables is to enable the users and developers of your plan to fully understand which pages link to each other. On a simple website this can be very simple, however, on larger scale websites this can be very complex.
Create a hierarchy document of this site, see if you can map it out on paper or on Word using the tools available in it. Website Production
Files that support this week | English:
Syntax - the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language. 0 |
Assessment:
Traffic Lights - Learners use green, amber and red traffic lights to indicate levels of understanding and to attract support from peers and the teacher. 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
1B.3 Produce a design for a four page interlinked website, with guidance, including an outline of the proposed solution. 1C.4 Prepare assets and content for the website, with guidance. 1C.5 Develop a website containing four interlinked web pages. with guidance 2C.P5 Develop a website contaming at least eight interlinked web pages. demonstrating awareness of purpose. 2C.P6 Test the website for functionality and purpose, repairing any faults, and documenting changes 2C.M3 Prepare assets and content tor the website demonstrating awareness of the users requirements. with all sources fully referenced. 2C.M5 Test interactivity and gather feedback from others on the quality of the website. and use it to improve the website. showing awareness of user requirements. 2C.D3 Refine the website. to improve accessibility and performance. taking account of user feedback and test results. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Formulae: using formulas, using words to express operations e.g. direction |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 6 | T&L Activities: Assignment Walkthrough - ASSIGNMENT 2 , your assignment has now bee given to you and it is important to take notes on how to tackle it. You should have now covered the key areas that are important to the success of a good design. The initial design stage of the creation of any project is overlooked by most, this is where the saying, "If you fail to plan, you plan to fail!" it true. Without setting yourself targets to achieve you have no understanding to whether you have achieved them or reached or completed.
In our Assignments, we will need to focus on identifying the following clearly.
Folder StructureWe need to demonstrate that we have a plan, this demonstration of knowing what we are doing also includes setting up our folders ready for the coming project and documentation. Let's think about our project, we will be creating a website, written work, using copies of examples of work from different units, images from off of the internet.
Storyboards
These will be a different way of laying out your site that you have been asked to create so that you have 2 options of how you might make your site look. Below is an example of an alternative design.
Files that support this week | English:
0 0 |
Assessment:
0 0 |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
1C.5 - Develop a website containing four interlinked web pages. with guidance 1C.6 - Test the website for functionality and purpose repairing any faults and documenting changes. with guidance. 2C.P5 - Develop a web site containing at least eight interlinked web pages. demonstrating awareness of purpose. 2C.P6 - Test the website for functionality and purpose, repairing any faults, and documenting changes 2C.M5 - Test interactivity and gather feedback from others on the quality of the website and use it to improve the website showing awareness of user requirements. 2C.D3 - Refine the website. to improve accessibility and performance. taking account of user feedback and test results. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 7 | T&L Activities: -Assignment Support- For 2A.P1: learners should explain the uses of two websites and the features they include, e.g. a theatre website that allows users to purchase tickets in advance using online payment methods, or a banking website that allows users to manage their bank accounts securely. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should have identified the intended uses of two websites and their features, including text, digital assets and links. For 2A.M1: learners should review how the features of the websites improve the presentation, usability, and accessibility, e.g. allowing users to customise the website format so that people with visual difficulties can enlarge the text. For 2A.D1: learners should look at the websites in more detail to discuss their strengths and weaknesses. They should discuss at least one strength and one weakness. Files that support this week | English:
Key terms Variable - In programming, a variable is a value that can change, depending on conditions or on information passed to the program. Typically, a program consists of instruction s that tell the computer what to do and data that the program uses when it is running. Operators - In mathematics and sometimes in computer programming, an operator is a character that represents an action, as for example x is an arithmetic operator that represents multiplication. In computer programs, one of the most familiar sets of operators, the Boolean operators, is used to work with true/false values. Array - In programming, a series of objects all of which are the same size and type. Each object in an array is called an array element. For example, you could have an array of integers or an array of characters or an array of anything that has a defined data type. |
Assessment:
Learning Capture - Teachers allocate time at the end of the session for the group to write down what they think they have learned. The information shared helps the teacher to see which content he may need to revisit and so shapes future planning. Got It? - Six techniques to help ensure effective transition from teacher instruction to independent work. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 8 | T&L Activities: For 2B.P2: learners should describe the purpose and user requirements for their website. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should identify the purpose and user requirements for their website. For 2B.P3: learners must produce a design for an eight-page interlinked website. The design documentation should include: â— the proposed solution containing: o a storyboard (with at least eight panels – one per web page) that outline the layout, content (e.g. text, assets and features) o a description of styles, templates, formats and interactive features o a site map including home page and file structure o a description of the ready-made and/or original assets to be used â— a list, in a sources table, of any original and/or ready-made assets â— a test plan, giving an outline of the range of tests to check the functionality of the website. Learners should include a collection of website ideas or prototypes in their designs. Learners should describe any styles, templates or formats, and include details of any interactive features. They should outline at least four different original and/or readymade assets that they intend to use, and list the sources for these assets in a sources table. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should design an outline proposed solution. The outline of a proposed solution will contain a website structure including at least four panels in a storyboard, a site map and an outline of two original or ready-made asset to be used. For 2B.M2: learners will be expected to add to their original design documentation by considering complex tools and techniques. Learners should include: â— how colour schemes and page styles will be applied consistently in all of the web pages â— how interactive components that make use of simple client-side scripting will be embedded, e.g. display a message to welcome the user, and how to make it easier for users to navigate. â— a brief outline of any alternative solutions for the intended website, e.g. the use of different assets for the intended website. These do not have to be fully worked-up designs. For 2B.D2: learners should justify their design decisions, including why alternative designs were rejected, explaining how the website will fulfil the stated purpose and user requirements. Learners must also think about the constraints, e.g. software availability and whether or not this will have an impact on developing the website. If it does, are there any alternatives for developing the same solution? Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Simple Peer Assessment - Learners complete work ready for formative or summative assessment by the teacher. Work is distributed to peers who assess the work by comparing it to criteria provided by the teacher. Coded Feedback - Teachers create simple codes to use as an integral part of formative feedback. The vast majority of the codes require specific actions to be taken by the learner to improve the quality of their work. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 9 | T&L Activities: For 2C.P4: learners should prepare assets (by gathering assets and creating them, if required), and list the sources for ready-made assets. At least four assets should be included, such as graphic images, audio clips and animations, as outlined in their designs. They should demonstrate an awareness of the purpose of the website. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should prepare their assets with guidance. Learners should include at least two assets in their websites. For 2C.M3: learners should prepare their assets and content for the website which has considered the user requirements of the website. All ready-made assets should be fully referenced in a sources table, with enough detail for another person to individually obtain the assets used. For 2C.P5: learners should use appropriate website authoring software develop their website using appropriate tools/techniques. They should demonstrate an awareness of the purpose and the website should be based on their designs. Learners should have developed a website that includes at least eight interlinked web pages with: â— at least four different assets â— internal and external hyperlinks â— text â— at least one table â— forms â— menus â— colour schemes and styles. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should have developed a website, with guidance, which includes at least four interlinked web pages, with text, a table, hyperlinks and two assets. For 2C.M4: learners should improve their website, taking account of usability and user requirements. Learners should include interactive components that make use of simple client-side scripting, e.g. JavaScript code that displays the date and time. An example of improving usability would be consistent colour schemes and styles in all web pages (using a method like cascading style sheets). For 2C.P6: learners will be expected to follow their test plans (as defined in their design) and test the functionality of their website, and check that it is fit for purpose. Learners are likely to experience technical difficulties as they develop their website. Learners will be expected to make the necessary repairs to their website. It is important that learners make appropriate comments on their designs and test plans about any issues they discover, and how they have resolved them. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should have tested the website for functionality and fitness for purpose. For this activity they will have needed guidance. For 2C.M5: learners should test the functionality of the interactivity features of the website. They should also test that the website meets the user requirements. Learners should complete user-experience testing, with the help of a test user. Learners should record this feedback as part of the testing process. While considering the feedback, they should keep the user requirements of the website in mind. Learners should use their feedback and test results to improve the website. For 2C.D3: teachers should recognise that the process of developing and testing a website is an iterative process. When making refinements to their websites, learners should take into account their test results and feedback from the ‘client’. Learners should refine their website using tools and techniques to cater for accessibility requirements and performance enhancements. For instance, learners could use: â— alternative text tags, text-to-speech to improve accessibility for users with hearing or visual impairments â— optimising assets to improve how quickly the website presents to the audience; if not appropriately compressed, video, animation and graphics can slow a website. Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Simple Peer Assessment - Learners complete work ready for formative or summative assessment by the teacher. Work is distributed to peers who assess the work by comparing it to criteria provided by the teacher. Just a Minute - At the end of the lesson teachers ask learners to summarise their learning. The comparison of these summaries against learning objectives informs planning. |
Learning Outcomes:
Review |
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 10 | T&L Activities:Assignment 4For 2D.P7: learners should explain why the product is suitable for the purpose and user requirements. Learners should give one reason for the purpose and one relating to user requirements. For level 1, as a minimum, learners should have identified how their website is fit for purpose, for example, ‘My website is suitable to advertise films as it includes posters for recent film releases and links to film company websites and local cinemas’. For 2D.M6: learners should build on the explanations given in the Pass criteria, and refer back to the user requirements and purpose as defined in their design. They should also seek feedback from users about the final website. An interview would be an ideal way of discussing the website with notes used to record the feedback. For 2D.D4: learners should evaluate the initial design ideas/prototypes against the final website in terms of overall user experience and ‘client’ requirements in the original brief. They should justify any changes that were made during development, and explain the rationale for any changes. They should also give at least three recommendations for improvements, but do not need to implement the enhancements. Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Just a Minute - At the end of the lesson teachers ask learners to summarise their learning. The comparison of these summaries against learning objectives informs planning. One-Minute Verbal Assessment - The teacher asks learners to prepare and deliver a one minute verbal summary of a forthcoming or completed activity, session or topic. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 11 | T&L Activities:RevisionFiles that support this week | English:
Test text |
Assessment:
Just a Minute - At the end of the lesson teachers ask learners to summarise their learning. The comparison of these summaries against learning objectives informs planning. Sentence Scramble - Learners unscramble sentences to check and develop their knowledge and understanding of content, punctuation and grammar. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 12 | T&L Activities: 12 Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Just a Minute - At the end of the lesson teachers ask learners to summarise their learning. The comparison of these summaries against learning objectives informs planning. |
Learning Outcomes:
12 |
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → |















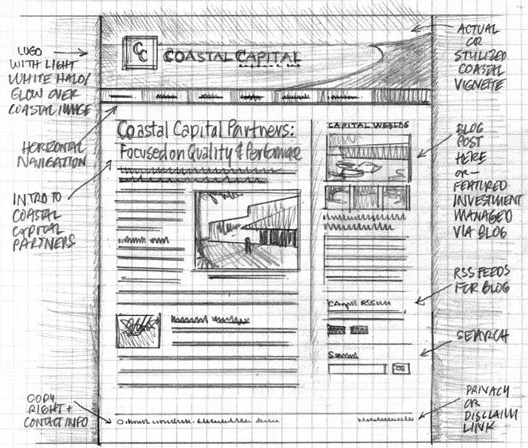


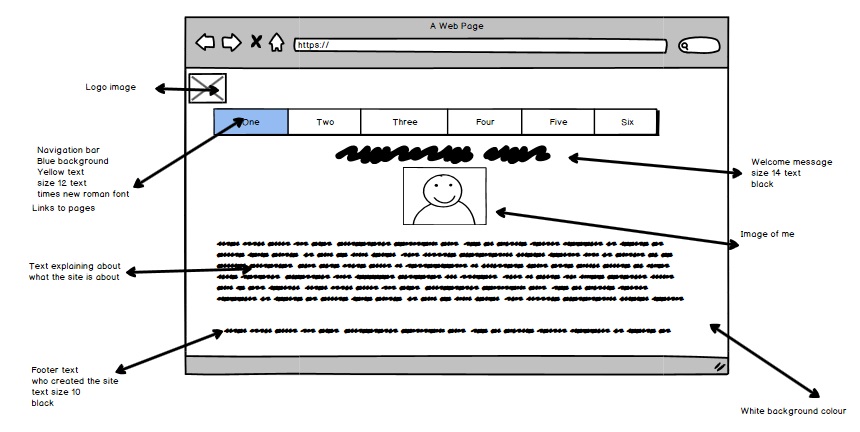 Alternative designs
Alternative designs