| Week 1 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: Summary of assessmentThis unit is externally assessed by a task set and marked by Pearson. The set task will be completed under supervised conditions in sessions: Part A is maximum of three hours of preparatory research and Part B is eight hours of task-based assessment. Part A needs to be completed in a two-week period before Part B, and Part B needs to be completed in the three-week assessment period timetabled by Pearson. The set task will assess learners’ ability to analyse an organisation’s aims and IT service needs. They will design an IT service solution by applying the IT service life cycle, while considering alternatives and the service management implications these may have on the needs of the organisation The number of marks for the unit is 68. The mark scheme will remain the same for each examination series. The availability of the task is December/January and May/June each year. The first assessment availability is May/June 2018.
Assessment outcomesAO1 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of IT service-delivery related facts, terminology, standards, concepts and processes AO2 Apply understanding of terminology, information technologies and procedures to explore outcomes and find solutions to IT service delivery problems AO3 Analyse data and information; recognise patterns, correlations and connections in order to solve IT service delivery problems and predict outcomes AO4 Evaluate technologies, procedures, outcomes and solutions to make reasoned judgements and make decisions about IT service delivery AO5 Be able to design an IT service delivery solution for an organisation with appropriate justification.
Contextual factors driving IT needs and services in organisationsExplore the purpose of organisations and how an organisation’s needs dictate the operational tasks to be performed and the IT services needed to support them. The application of the IT service life cycle is then used to design an IT service delivery solution. A1 IT service life cycleUnderstand that the IT service life cycle can be applied in a number of project management methodologies, including: (Links to unit 9) PRINCE2, PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a project management methodology widely used in the UK and many other countries.
Agile, rapid application development (RAD), lean and waterfall.
Be able to apply the principles and concepts of the IT service life cycle when defining and analysing IT service delivery requirements in a range of organisations and contexts:
discussion: explain the IT service lifecycle and how it is compatible with most project management methodologies including Prince2, Agile, RAD, Lean and Waterfall.
• Service identification:
o producing an outline IT service strategy
o identifying and prioritising the needs of organisations, users and customers
o producing an outline IT service catalogue.
Individually investigate how failure to provide service delivery can impact the organisation‘s brand image and the customer experience, by considering some recent examples (not necessarily about IT service delivery, but about service delivery in general). Small group work: work in groups to investigate the key aspects of the IT service delivery design:
Service delivery design: defining the technical requirements for appropriate IT service delivery and planning solutions to facilitate identified needs. Paired work: use the internet to find an example of the IT Service Delivery Life Cycle. Create an annotated diagram of one version and compare it with project management methodologies in general. For example: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc543217.aspx
Complete page 1 - Project Methodologies and 2 - Service Identification & Design of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
• Service management, through continual review and refinement of IT service delivery needs and related solutions: o analysis of benefits and drawbacks for organisations of a solution in terms of meeting an organisation’s IT service delivery needs o analysis of alternative solutions and justification of suggested actions or solution o analysis of the impact of implementation and the ongoing operation of the IT services o evaluation of the potential success of a service solution and justification of improvement(s).
Complete page 3 - Service Management Reviews of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
The key benefits to an organisation of effective application of the IT service life cycle to facilitate IT service delivery, including: • adherence to standards • automation of processes • continuity and availability of service • customer attraction and retention • disaster prevention and recovery • improved data or system integrity, productivity, and/or services and products • interoperability of services/systems • optimised security • reduction of operational costs • simplification of processes.
Complete page 4 - Benefits of Effective IT Service Life Cycles of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
The roles and functions of key staff to facilitate the effective implementation of the IT service lifecycle, including: architects, developers, project managers, technicians, service desk personnel.
Complete page 5 - Roles of Key Staff of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator Length, weight, capacity, temperature: Measuring, using scales, ruler, tape measure, thermometer Recording and comparing results, converting, Choosing appropriate units and measuring instruments, estimating. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 2 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: A2 Purpose and functions of organisationsApply an understanding of IT systems and the IT service lifecycle to identify the IT service delivery requirements of organisations in a range of sectors and vocational-based scenarios.
discussion: what are the key components of service delivery management? The website provided below lists key factors such as service culture, employee engagement, service quality, customer experience. • Understand the purpose and differences of organisations that provide a service and/or a product. Different formats of organisations such as sole traders, partnerships, companies, charities and franchises as well as a range of sectors in which these organisations operate such as primary, secondary and tertiary sectors. Each sector can then be further broken down using examples such as finance, building, manufacturing, aerospace and engineering, technology, government and agencies, energy, food, transport, telecommunications, services such as hairdressing or beauty therapy, health care, marketing, agriculture, science and innovation, defence, arts and media, hospitality and catering, sports etc. Learners must be able to identify the difference between organisations providing products and those providing services. group activity: each group should select three sectors to investigate. During the investigation you should identify the types of IT service delivery these sectors or areas might need (e.g. science and innovation will need simulation software, analytical software and be able to handle significant volumes of data, security will also be a key factor due to commercial sensitivity). You should identify key activities that businesses in each of these sectors will undertake (e.g. diary management, scheduling, invoicing, data handling). **
split into three groups, then into small subgroups. Each group should explore one of the following allocated case studies:
discussion: after the small group activity , whole class discussion, where you should be able to identify the similarities in the issues identified across the studies, as well as any similarities in approaches to the solutions. You should be able to explain following: • Understand that IT service requirements are driven by the priorities of an organisation and how this impacts on IT service delivery requirements.
• Be able to identify and define the features of and characteristics of IT services required for the key tasks carried out by functions of an organisation: o manufacturing of products o delivering services o supply chain management o marketing and sales o customer relations o resource management o staff recruitment o staff management o support and financial
group activity: using the research from the previous small group activity, identify which of the activities are likely to have the highest priority. You should be able to identify business’ critical activities as well as administrative and support tasks that carry a lower priority. You should, e.g. be able to identify the importance of IT service delivery in supporting manufacturing activity that would be critical to a manufacturing company of any type, or health-monitoring technologies in a hospital. The outcomes of your investigation should be presented in any format (PowerPoint, handout, short video etc). ** Complete page 6 - Purpose and Function of Organisations of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES Files that support this week | English:
Reading: Read and understand texts, selecting material appropriate to purpose, collating from different sources and making comparisons and cross-references as appropriate. Writing: Write to communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, using and adapting forms and selecting vocabulary appropriate to task and purpose in ways that engage the reader |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Using numbers: Written or mental methods, using a calculator, rounding and estimating, problem solving Organising and Representing data: Drawing tables, charts and graphs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 3 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: A3 Service identificationApply understanding of IT systems to analyse the IT service delivery requirements in a range of organisations and to be able to define an outline IT service strategy. • Be able to define an organisation’s IT service delivery requirements by drawing on knowledge of: o the purpose and type of organisation o the aims and goals of the organisation o customer experience, including: – the services or products the organisation or function provides – the organisation’s customers: needs, expectations, how product/service is delivered and will be consumed o staff: needs, working styles and patterns Lead-in: IT service life cycle depends on a range of key staff who undertake specific roles in the process. This includes:
Using this website provide a very top level definition: http://careers.simplicable.com/careers/new/87-information-technology-job-descriptions
group work: each group should be allocated one of the roles to investigate. Learners should use the internet to find an advertisement for the role they have been allocated. Through this they will be able to explore job descriptions (including roles and responsibilities) and person profiles. o location: staff, customers, premises, market/service delivery point.
Complete page 7 - Service Identification of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
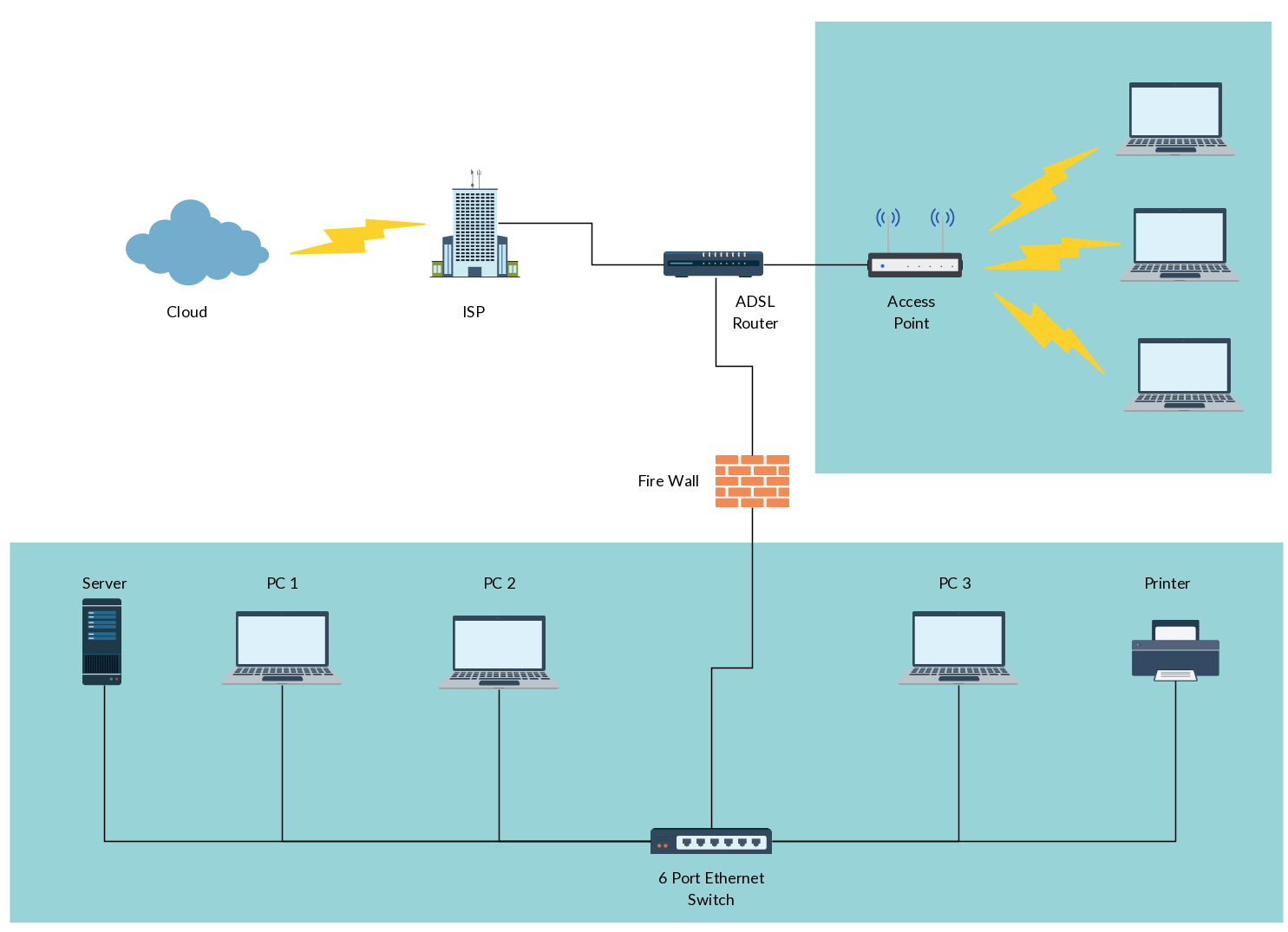
• The use, application and interpretation of diagrams to identify and represent the IT service (and related data and information) requirements of an organisation: o functional charts
o data flow diagrams
o building/floor plans
o network diagrams.
Complete page 8 - Using Diagrams to Represent IT Servicesion of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
• Understand the contextual factors that affect the needs of an organisation and the identification of IT service requirements, to include: o user and/or customer needs and expectations o changes in demand for products and services o scalability of the organisation and/or service(s) to meet the demand o the moral and ethical considerations for organisations, including: – monitoring of staff/user activity – privacy concerns – environmental – freedom of speech/censorship – the purpose, content and enforcement of acceptable use policies
Complete page 9 - Contextual Factors Affecting the Needs of an Organisation of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
o current and relevant legislation applying to the use of IT systems: – Computer Misuse Act 1990 – Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 – Data Protection Act 1998 – Telecommunications Act 1984 – Interception of Communications Act 1985 – Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 – Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992 – Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act 2000 and Lawful Business Practice Regulations – Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Regulations 2013 o security considerations o developments in technology o accepted and/or standard ways of working. Complete page 10 - Current Legislation of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Speaking:Speak to communicate clearly and purposefully; structure and sustain talk, adapting it to different situations and audiences; use Standard English and a variety of techniques as appropriate Listening: Listen and respond to speakers ideas and perspectives, and how they construct and express meanings Sentence Structure: Use a range of sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate punctuation and spelling. |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Statistic extracting information: Tables, Diagrams, Charts and Graphs Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator Time: Reading clocks and calendars, using timetables, organising appointments, conversions, dates |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 4 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: B IT service delivery designB1 Defining IT service delivery requirementsApply understanding of IT systems to analyse the IT service delivery requirements in a range of organisations and to be able to define the technical requirements of a solution to effectively deliver IT services throughout the IT service life cycle. Be able to produce an IT service catalogue to define the services and service requirements of organisations in line with relevant functions and processes of an organisation: • service name • service description, to include: o what needs to be achieved o overview of purpose of information and data required (and by whom) to effectively deliver the service o overview of technologies required.
Complete page 13 - IT Service Catalogues of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Statistic extracting information: Tables, Diagrams, Charts and Graphs Using Numbers: Counting, Place value, adding and subtracting, multiplying and dividing. Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 5 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: B2 Considerations when defining IT service delivery requirementsUnderstand the benefits and constraints of contextual factors that affect the needs of an organisation and the impact on definition of IT service delivery requirements, to include:technology,
costs,
environmental,
ethical,
legal,
location,
moral,
risks,
scalability,
security and sustainability.
EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES Files that support this week | English:
sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command Sentence Structure: Use a range of sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate punctuation and spelling. Interactive Speaking : Interact with others, shaping meanings through suggestions, comments and questions and drawing ideas together. |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Question and Answer - Verbal discussion with learners to quantify understanding
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator Statistic extracting information: Tables, Diagrams, Charts and Graphs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 6 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: B3 Designing an IT solutionApplying understanding of IT systems to analyse the IT service delivery requirements in a range of organisations to be able to design an IT service delivery solution. Design an effective IT service delivery solution to meet the needs of an identified organisation that provides coverage of:Information requirements
Data requirements
Hardware and software service options
Managing infrastructure and users.
EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Voice: Opportunities within lesson to develop their own reflective writing as well as develop technical writing skills within the production of their treatment. Writing: Write to communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, using and adapting forms and selecting vocabulary appropriate to task and purpose in ways that engage the reader Reading: Read and understand texts, selecting material appropriate to purpose, collating from different sources and making comparisons and cross-references as appropriate. |
Assessment:
Question and Answer - Verbal discussion with learners to quantify understanding Product Evidence - Learners to create product evidence to demonstrate understanding
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Length, weight, capacity, temperature: Measuring, using scales, ruler, tape measure, thermometer Recording and comparing results, converting, Choosing appropriate units and measuring instruments, estimating. Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 7 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: B4 Considerations when designing an IT service delivery solutionLearners should be able to apply understanding of IT systems to evaluate the appropriateness of IT service delivery solutions in meeting the needs of an organisation in comparison to alternatives. Understand the implications and considerations for organisations of the selection of, and dissemination of, information and data
Compatibility
When implementing or planning an IT service/improvement or upgrade it is essential to ensure that Compatability is reflected on. Systems that are incompatible can produce a number of potential issues other than the obvious of not working. Systems can ave the potential to have a knock-on effect to systems that are not directly linked to the implementation that is being installed. For example the installation of a new network firewall, this could be a simple installation of a piece of hardware, that was being implemented to reduce the potential from attacks outside of the network, however the system has now stopped a server that sends information to clients from being able to access the internet, and this server cannot communicate with the hardware because it is a specialist "Cisco" or "Huawei" device. The cost implication could be large as the company would now need to find a compatible version that works with both systems. Case studies of this type of occurrences are available, for example, the NHS and its legacy systems only being able to work on windows internet explorer 5.
Corporate message
Cost, processing
Productivity
Privacy
Reliability
Security
Size/quantity
Quality
User and/or customer experience, to include ease of use, performance, availability, accessibility
User and/or customer needs
Working practices.
Understand the implications of selecting data and information sources and methods of dissemination that influence the design of IT service delivery solutions.
Understand the implications for organisations of the factors affecting the use and selection of software and hardware to meet IT service delivery requirements: availability, cost, connectivity, capacity, ease of use, features, privacy, scalability and usability.
Understand the implications for organisations of the factors affecting the use and selection of software and hardware to meet IT service delivery requirements.
Understand how the use and selection of software and hardware influence the design of IT service delivery solutions.
Understand the implications for organisations of the management of IT service delivery to meet IT service delivery requirementsAsset management
Identification of asset utilisation to analyse effectiveness and efficiency
Managing updates and upgradesWhen a company installs any update or upgrade to a system it is important to assess the impact of these. I most cases updates and upgrades improve performance, security, and in a small number of situations presentation. However, these do come with potential pitfalls and drawbacks. The installation of an update or upgrade to a system that is old could cause issues with compatibility for both hardware and software resulting in downtime and or corruption to data and/or operating systems. Therefore it is good practice for most companies to test these implementations prior to them being "rolled out". In small company situations, it may be that they are unable to test the installation of the updates/upgrades, so in this instance, a sufficient disaster recovery process would need to be followed, for example, back-ups of data to external sources. In larger corporations company may be able to use test environments to do this, or, create copies of virtualised servers and run test deployments to see the stability of them. If implemented well companies can introduce these updates and upgrades in a phased timetable where they trickle them to users and then this would reduce potential downtime.
Installation and/or deployment
Security issues and procedures, including:
– physical security when looking at the implementation of an IT service such as server hardware and equipment, consideration must be given to the access to these devices/services as they have the capability to hold company sensitive data on them let alone client data. The security measures that need to be put into place must ensure that the right people and only the right people have access. For example, within a doctors surgery you would not allow doctors and general staff access to the physical servers, you would only allow them a rights restricted access through software and applications, however the designated IT technical person would need access, so you would enable their key card to access the room in which the server was in. Again however this individual shouldn't be able to access the data so they could have a technical login to the server that only provides them with the ability to make administrative changes and updates, this would also mean that the USB, floppy and CD drives are all disabled or have physical locks to prevent removal of data. – security issues relating to the use of traditional, mobile and cloud-based technologies
– security software
Current and relevant legislation
Computer Misuse Act 1990The Computer Misuse Act was introduced partly in reaction to a specific legal case (R v Gold and Schifreen) and was intended to deter criminals from using a computer to assist in the commission of a criminal offence or from impairing or hindering access to data stored in a computer. The Act contains three criminal offences for computer misuse: -
The Crown Prosecution Service offer further guidance in relation to the Computer Misuse Act.
Data Protection Act 1998
The Data Protection Act regulates the use of personal data by organisations. Personal data is defined as information relating to a living, identifiable individual. The Act is underpinned by eight guiding principles: 1. Personal data shall be processed fairly and lawfully. 2. Personal data shall be obtained only for one or more specified and lawful purposes, and shall not be further processed in any manner incompatible with that purpose or those purposes. 3. Personal data shall be adequate, relevant and not excessive in relation to the purpose or purposes for which they are processed. 4. Personal data shall be accurate and, where necessary, kept up to date. 5. Personal data processed for any purpose or purposes shall not be kept for longer than is necessary for that purpose or those purposes. 6. Personal data shall be processed in accordance with the rights of data subjects under this Act. 7. Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data. 8. Personal data shall not be transferred to a country or territory outside the European Economic Area unless that country or territory ensures an adequate level of protection for the rights and freedoms of data subjects in relation to the processing of personal data.
GDPRGDPR legislation came into Law on the 25th of May 2018, where it replaced the Data Protection Act of 1998. This Legislation was designed to reflect the inclusion of the way in which our data can be used and moved around the world using digital means. The below video demonstrates the changes that companies needed to consider prior to its implementation as the new legislation carried a severe fine if companies were found to be non-compliant. In the UK, the Information Commissioner's Office can now issue fines of up to 4% of a company's annual turnover, or 20 million (whichever is greater) for the worst data offences.
Ethical and moral issues
Staff trainingWhenever and where ever new software or hardware systems are implemented it is best practice to provide clear and appropriate training and demonstrations to the staff team. It is vital to a company that the employees are able to continue to do their jobs and smoothly as possible and any new system is able to complement or improve the operators' jobs. User training is also beneficial to a company as is informs the users of what is expected and what most importantly is NOT. Users/operators will normally be able to provide good feedback to managers and developers of any potential flaws or issues that can/have occurred so that these bugs can be resolved and repaired.
Customer support processes and implications of user problems and IT equipment faults
Challenges faced by organisations when responding to changes in user needs:additional or changes to services, network expansion, emerging technologies,changes in legislation and security and privacy issues.
Complete page 14 - Considerations when Choosing Software and Hardware, and 15 - Considerations when Designing Solutions of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Sentence Structure: Use a range of sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate punctuation and spelling. Listening: Listen and respond to speakers ideas and perspectives, and how they construct and express meanings Organising Information: Organise information and ideas into structured and sequenced sentences, paragraphs and whole texts, using a variety of linguistic and structural features to support cohesion and overall coherence. |
Assessment:
Just a Minute - At the end of the lesson teachers ask learners to summarise their learning. The comparison of these summaries against learning objectives informs planning. Question and Answer - Verbal discussion with learners to quantify understanding
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Collect and record data: Questionnaires, Observation, Tally Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 8 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: C Information and data requirements of organisationsHow and why information and data differs depending on the intended use, and the type and size of the organisation.
C1 Information in an organisationHow and why organisations use and disseminate information at different levels of the organisation and their effect on IT service delivery.
Analyse information requirements at different levels of the organisation:Strategic-level information used to inform longer-term and holistic decision making across different functions of an organisation
Management-level information to inform shorter-term and operational decision making across different functions of an organisation
Operational-level information to inform the day-to-day actions of different functions of an organisation.
Complete page 19 - Analysing Information at Different Levels of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
Analyse information requirements in organisations of varying size and type to identify why information is used:Defining the scope of a customer’s needs
Managing day-to-day tasks and services
Ensuring continuation and provision of service and/or product
Identifying and planning improvements:
– setting and developing policy – communication with staff, colleagues and/or customers.
Be able to analyse organisations of varying size, type and purpose to identify sources of information used by: customers and/or clients, IT support team, management team/team leaders and other staff.Complete page 21 - Analysing Information at Varying Organisation Sizes of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Listening: Listen and respond to speakers ideas and perspectives, and how they construct and express meanings Reading: Read and understand texts, selecting material appropriate to purpose, collating from different sources and making comparisons and cross-references as appropriate. Organising Information: Organise information and ideas into structured and sequenced sentences, paragraphs and whole texts, using a variety of linguistic and structural features to support cohesion and overall coherence. |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Question and Answer - Verbal discussion with learners to quantify understanding
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Statistic extracting information: Tables, Diagrams, Charts and Graphs Organising and Representing data: Drawing tables, charts and graphs Length, weight, capacity, temperature: Measuring, using scales, ruler, tape measure, thermometer Recording and comparing results, converting, Choosing appropriate units and measuring instruments, estimating. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 9 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: C2 Data in an organisation• Understand the interrelationship (and differences) between information and data and how this affects the information generated.
• Understand the features, characteristics and implications of the requirements for data at different levels of an organisation.
• Be able to analyse data used to define service requirements and devise IT service delivery solutions.
• Be able to define the scope of the data needs at different levels of an organisation in relation to: o sector and type of the organisation o size of the organisation o services and/or products the organisation provides o aims and goals of an organisation o customers o staff o location o operational tasks, including those performed by individuals and IT services and systems. Complete page 20 - Role of Data and Information of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
• Be able to analyse the data source and data set requirements of organisations and describe IT service delivery solutions in relation to an organisation’s service requirements: o volume – the quantity of data that is generated o velocity – the speed of generation of data o variety – the mixture of data to be processed. Complete page 22 - Volume, Velocity and Variety of Data of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Sentence Structure: Use a range of sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate punctuation and spelling. Interactive Speaking : Interact with others, shaping meanings through suggestions, comments and questions and drawing ideas together. Voice: Opportunities within lesson to develop their own reflective writing as well as develop technical writing skills within the production of their treatment. |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator Statistic extracting information: Tables, Diagrams, Charts and Graphs |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 10 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: D Facilitating IT service deliveryThe concepts, features and implications of the use of software and hardware as part of an IT service delivery solution. D1 Software service options• Understand the features and use of software services to support typical uses of IT service(s), including: o communication o collaboration o virtualisation and containerisation o product production and/or service provision o financial transactions o file storage and/or transfer o platform/service hosting o productivity o remote access o creativity and/or innovation o customer access to product and/or service o data collection and analysis (including metrics) o performance analysis (including metrics).
Complete page 25 - Software Service Options of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
• Be able to analyse the needs of an organisation and identify the types of software, and the features that would be used, to meet IT service delivery requirements: o operating systems: - When providing an IT service solution to a client, you need to provide information to the operating systems that will be implemented. Your client can be using specific hardware that is only compatible with some operating systems, for example, Apple's OS would only be able to be installed on the apple server hardware to be able to fully optimise the resource and in some instances, for it to run at all, this may have a cost implication. If a client has a budget limitation they may find that open-source operating systems would be the best fit for them, for example, Red Hat Linux, Ubuntu server or any other distribution. o utility software
o application software, including content management systems and expert systems In some instances companies may require application software to be used internally, this can range from training software to SAGE accounting software. These systems may require additional hardware to run, for example, a web server. However, this could be negotiated by using software-based emulation called virtualization. Where might a company use a content management system? In most companies, employees when starting employment and or during their employment will be required to undertake core training that could be delivered using content management systems where the users access material, quizzes and upload work to prove that they have participated in the training requirements for them to do their work.
o combining tools and applications.
Complete page 26 - Analyse the types of Software Needed of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment
• Be able to analyse the needs of an organisation and describe the use of open-source and proprietary software as part of an IT service delivery solution that takes into consideration relevant contextual factors, including: o customisation o expertise o functionality o implementation/deployment o interoperability o performance o scalability o stability o support.
Complete page 27 - Analyse Open-Source and Proprietary Software needed of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
|
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator Analysis of information: Interpreting Results, Drawing conclusions from data, Comparing data |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 11 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: D2 Hardware service options• Understand the features and use of, and relationships between, different hardware that form part of an organisation’s entire IT infrastructure, to support typical IT service delivery requirements. • Understand the features and use of, and relationships between, different methods of providing connectivity between devices and systems to support an organisation’s IT service delivery requirements. Complete page 28 - Hardware Service Options of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment • Be able to analyse the needs of an organisation and describe the use of hardware as part of an IT service delivery solution that takes into consideration relevant contextual factors, including: o user factors: – number and location of users – user experience – ease of use, performance, availability, accessibility – user needs o organisational factors – size of organisation, geographical spread, layout of buildings, tasks to be performed and future developments and diversification o technological factors – emerging technologies, existing equipment/infrastructure/software, capacity required and maintenance o general factors: – user and customer expectations – security – budget – connectivity – cost – efficiency – implementation – timescales, testing, migration to new system(s) – productivity – security – scalability Complete page 29 - Analyse the Hardware Needed of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES Files that support this week | English:
Reading: Read and understand texts, selecting material appropriate to purpose, collating from different sources and making comparisons and cross-references as appropriate. Writing: Write to communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, using and adapting forms and selecting vocabulary appropriate to task and purpose in ways that engage the reader |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Length, weight, capacity, temperature: Measuring, using scales, ruler, tape measure, thermometer Recording and comparing results, converting, Choosing appropriate units and measuring instruments, estimating. Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Week 12 | T&L Activities: Learning Aims and Objectives: D3 Managing IT service delivery solutions and the implications of changeUnderstand the concepts and challenges of managing infrastructure, users and IT services in an organisation to meet current and future needs and priorities. • Be able to analyse the needs of an organisation and describe how IT infrastructure, services and users will be managed as part of an IT service delivery solution that considers relevant factors, including: o user management and support o customer management and support o product/service delivery o asset management o changes in product/service o changes in organisational needs/aims o incident management o performance metrics, including collection and analysis. • Understand the role and implications of acceptable use policies on the provision and management of IT service delivery solutions.
• Understand the implications for organisations of using in-house and external systems for provision of IT service delivery solutions, including: o service-level agreements (SLAs) o hardware and software requirements o cost o availability o scalability o legal ownership of data and jurisdiction o problems encountered by data and processing residing in multiple jurisdictions o issues relating to data and processing residing regions that may not have appropriate laws covering protection and use of data o implementation. Complete page 31 - Using Internal and External Systems to Manage Change of your Onenote class activities, it is essential that you complete this as this will provide revision notes towards your end of unit assessment EXAM PREP - REFER TO PAST PAPERS AND STUDENT EXAMPLES
Files that support this week | English:
Listening: Listen and respond to speakers ideas and perspectives, and how they construct and express meanings Reading: Read and understand texts, selecting material appropriate to purpose, collating from different sources and making comparisons and cross-references as appropriate. Writing: Write to communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, using and adapting forms and selecting vocabulary appropriate to task and purpose in ways that engage the reader |
Assessment:
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria. |
Learning Outcomes:
|
Awarding Organisation Criteria:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maths:
Money: Budgeting, Estimating, Rounding to nearest pound, using correct symbols, calculating costs using a calculator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stretch and Challenge:
|
E&D / BV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Homework / Extension:
|
ILT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| → | → | → | → | → | → | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||