week 4
Hardware components
There are many main hardware components inside a personal computer, we will look at these, what options you might have, and their typical costs.
The main hardware components found in a PC are;
Storage
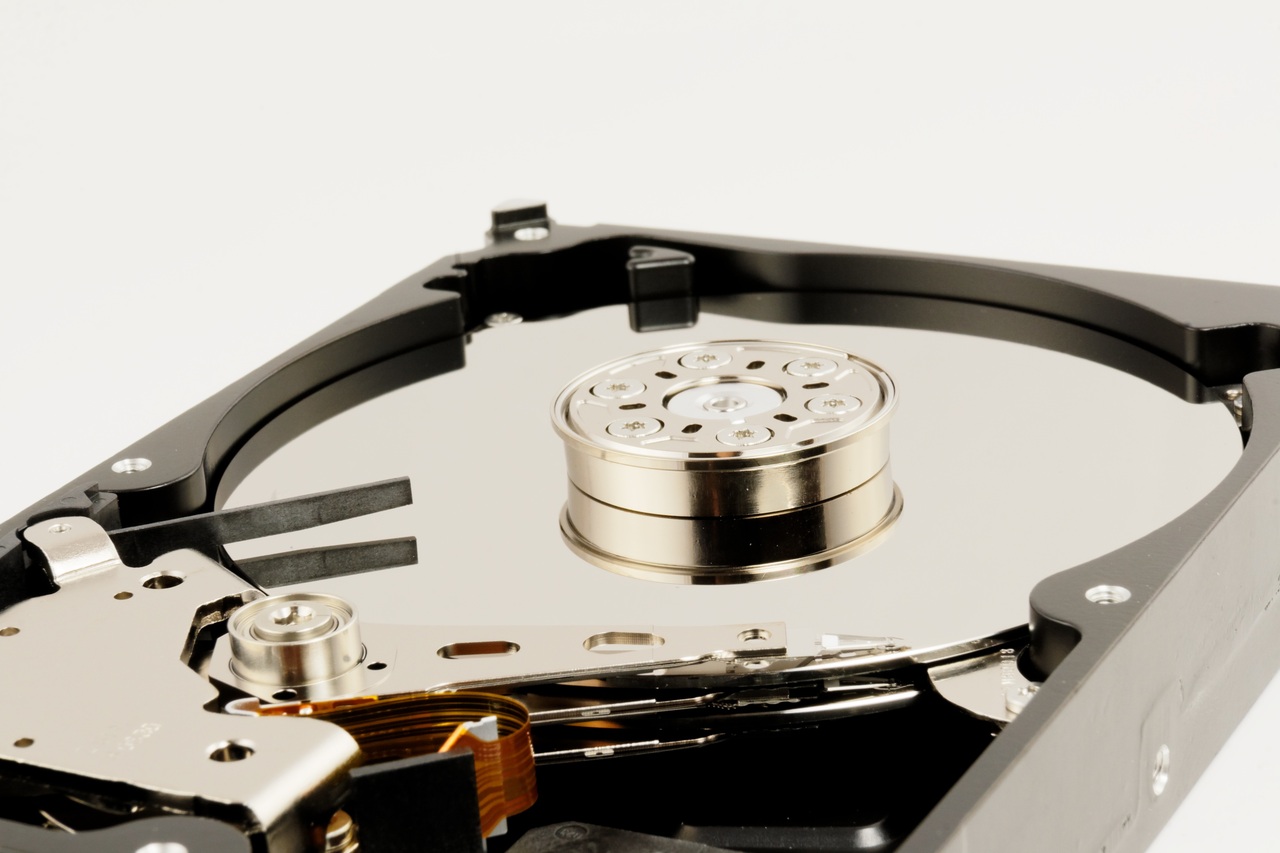

As discussed earlier the storage devices that can be used on a computer can be varied. This could be down to the age of the PC motherboard and the cost implications. The storage that is selected to go inside of a PC has to be considered, as the technology can have limitations and capabilities, these are, speed of storage or and retrieval of data. In standard HDD drives the use of spinning disks and magnets is commonplace, these spin at 5200 rpm (rotations per minute) for laptop 2.5-inch drives, or, 7200 rpm for standard 3.5-inch drives.
In the case of an SSD drive, there are no moving parts and as a result, data is saved to a chip, this means that the data can be transferred sat lightening speeds.
Input and output connectors
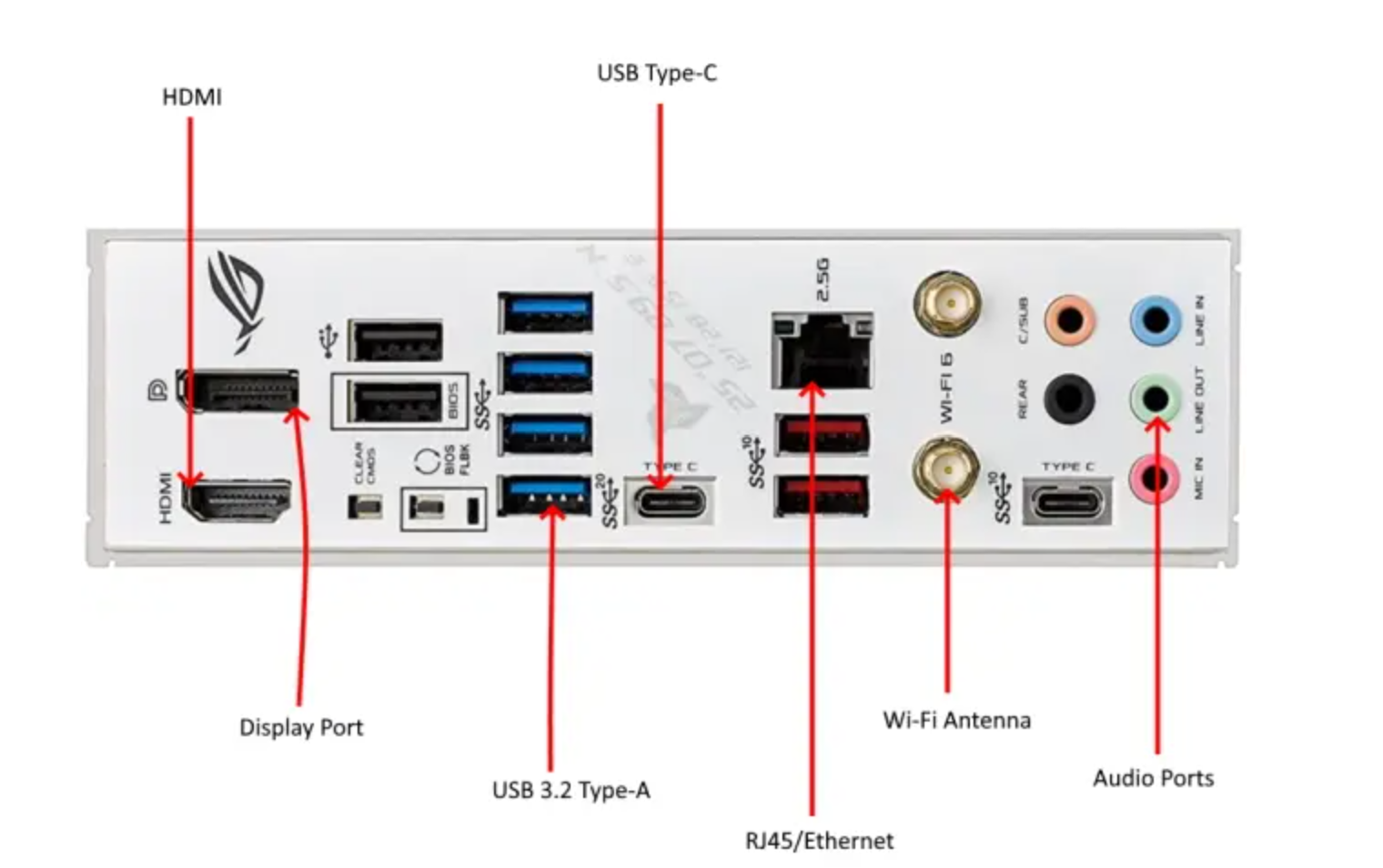
Inputs and outputs can be different from each PC's use case. However, there are some standard "IO" found on most motherboards, such as USB (Universal Serial Bus) this includes newer connections such as USB C, AUX Jacks (Headphone, Microphone and Audio in), Serial and Parallel input/output, VGA (Video Graphic Adapter), HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
External data connection
e.g. wireless (802 standards), Bluetooth, wired connection type
Memory

Memory is best known as RAM or Random Access Memory. Used in a PC memory is a piece of hardware that acts as a temporary data store for applications to use. Consider it as short-term memory you have for example being told a phone number to pass on to another person. The benefit of this is that the PC can assess this very quickly and as a result it can undertake operations very fast. The more memory a system has the more operations it can do quickly. However caution must be taken, because memory is temporary and not permanent, once power has been cut the memory module will forget the data that it had in it, so for example, if you had been working on a Word file and hadn't saved it and then the power is cut all your work will be lost. The only way to ensure that this data is not lost is to move it to pertinent storage, which is saving it to the HDD, SSD or other storage devices.
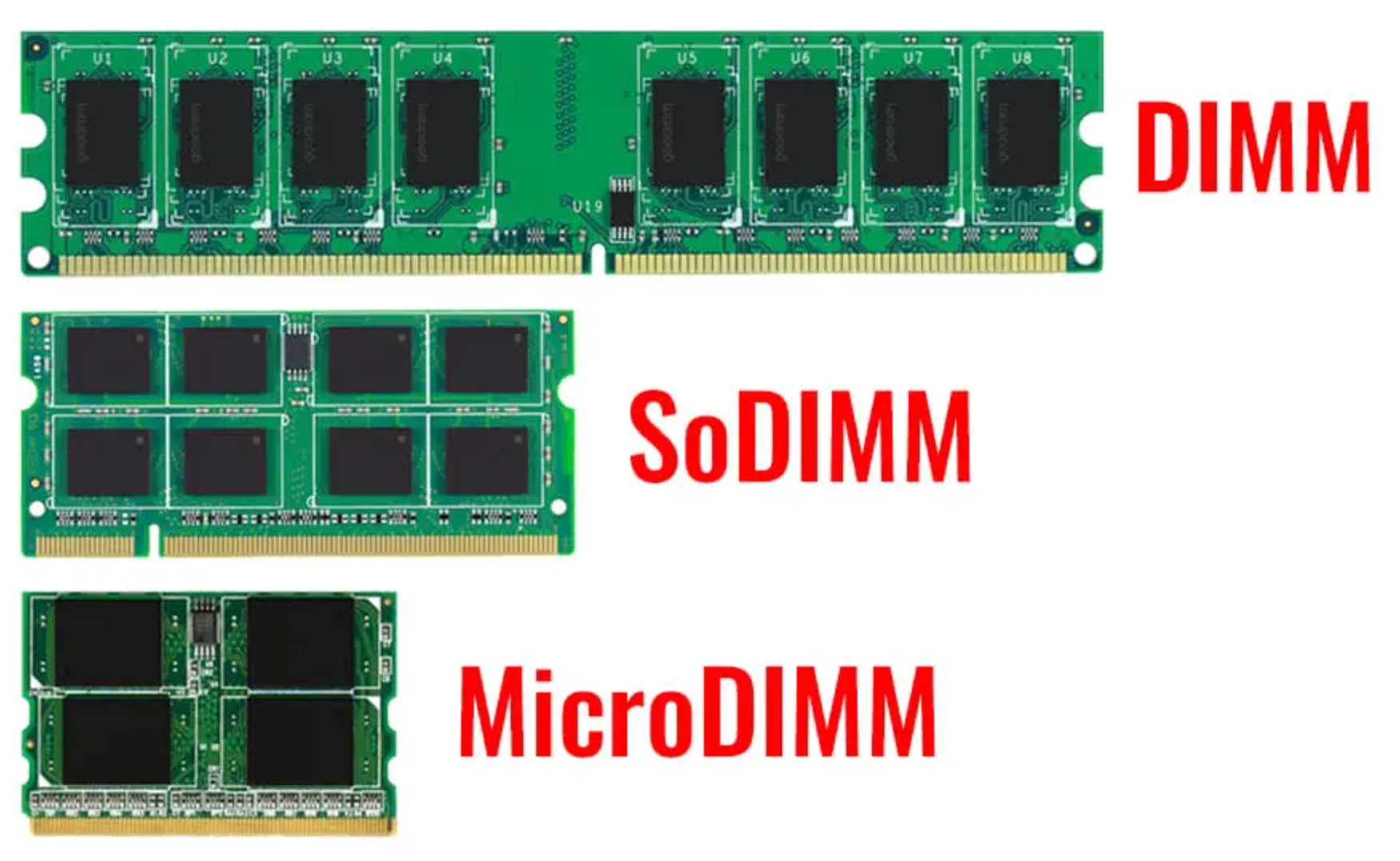
Memory can come in different shapes and sizes,
TYPES
SODIMM - these are mainly used in laptops as they are a smaller physical size
DIM - Normally found in most PCs
GENERATIONS
SIM - Single Inline Memory
DIM - Dual Inline Memory
DDR - Double Data Rate
DDR2 - Double Data Rate 2
DDR3 - Double Data Rate 3
DDR4 - Double Data Rate 4
DDR5 - Double Data Rate 5
GDDR
e.g. clock rate of memory, capacity of motherboard, capacity of memory, socket type, solid state versus dynamic memory
Other important hardware
There are a number of other important hardware elements required to create a functional personal computer, these include;
- data bus types -
- case - the case is an important element of the PC as it not only contains the internal elements of the computer, but it also protects them from things like accidental damage from spillages and or others that might put their hand inside un-necessarily. Another factor that the case is used for is cooling as the internal temperature needs to be regulated so that the PC performs at its optimum.
- heat sinks and fans - These devices are all part of the cooling systems used to ensure that the components do not overheat.
- power supply unit - Often referred to as the PSU, the power supply unit is the provider of electricity to the system. The PSUs available today provide modular ports so that only the required number of cables needed are present. Historically old PSUs had multiple cables available, however in most situations, these were not needed, and, as they were left inside the case could get snagged into fans or disrupt airflow around the cooling of the other internal components.
Last Updated
2024-03-07 09:40:54
Links to Learning Outcomes |
Links to Assessment criteria |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Learning aim B: Produce a plan to build a personal computer |
1A.1 Identify the uses of at least two different personal computers and determine the cost to build each computer.
2A.P1 Explain the uses of at least two different personal computers and determine the cost to build each computer.
2A.M1 Review how the processor choice for a personal computer can affect performance.
2A.D1 Discuss how the specification for a personal computer can affect performance. |
English
Maths
How 2's Coverage
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria.
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria.
Files that support this week
Week 3←
PrevWeek 4←
PrevWeek 5←
Prev→
Next→
Next