week 10
3.10 Data models3.10.1 Know the types of data models and understand how they organise data into structures:
Data models describe how data is structured, stored, related, and accessed within a system. They act as blueprints that define how information flows, how tables or objects connect, and how systems interpret and manage data.
In Digital Support and Security, data models are essential because technicians rely on structured information to manage devices, users, logs, permissions, and security events. The better the data is organised, the easier it is to maintain system integrity, detect incidents, troubleshoot faults, and ensure compliance with policies like GDPR or access-control rules.
Below are the main data models used in modern IT support and security environments, with explanations, structures, and industry-linked examples.
Hierarchical
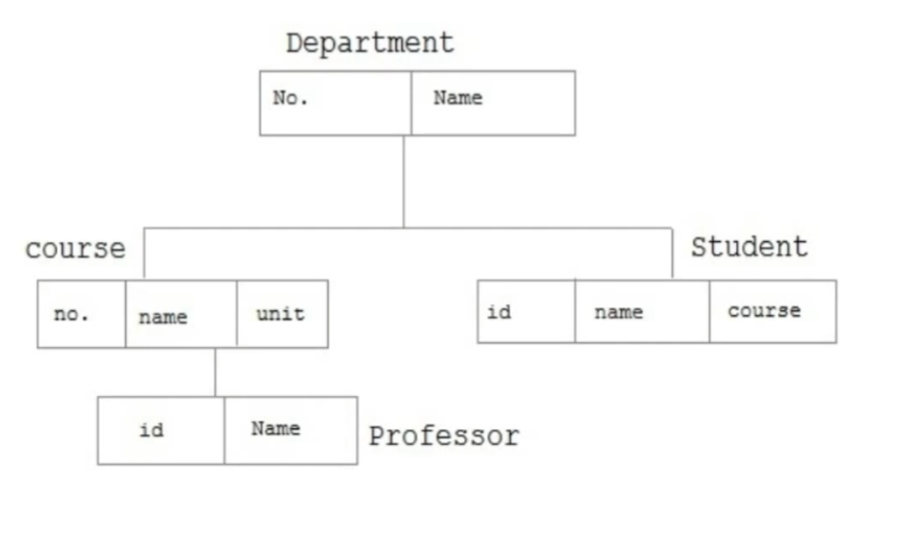
This model organises data in a tree-like structure, with parent–child relationships.
How it Organises Data
-
Each child has one parent.
-
Data flows in a single direction.
-
Works well for data that naturally forms a hierarchy.
Digital Support & Security Example
Active Directory (AD) uses a hierarchical model:
-
Organisation → Domains → Organisational Units → Users/Devices
This makes it easy to apply security policies (GPOs), permissions, and access-control rules at different levels.
Strengths
-
Clear structure
-
Fast traversal
-
Ideal for logical grouping
Weaknesses
-
Not flexible
-
Hard to represent many-to-many relationships
Network
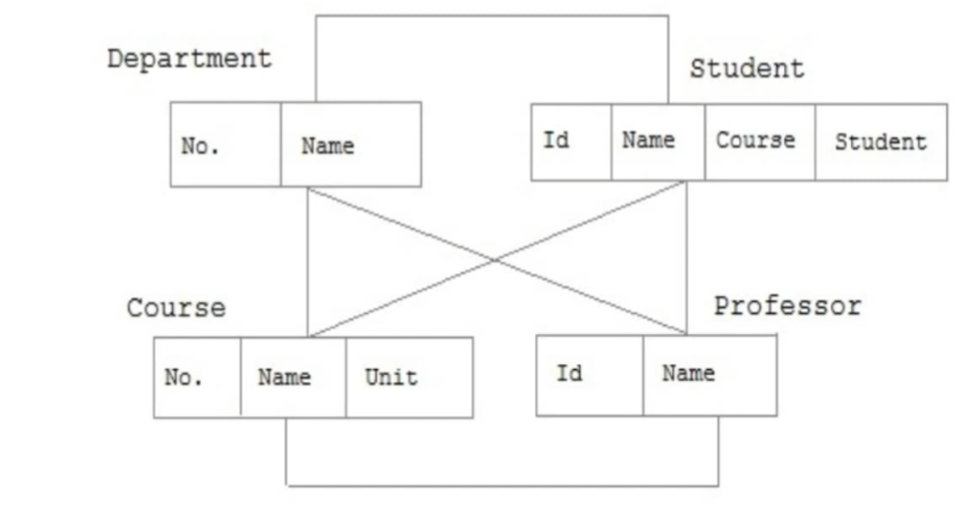
A flexible model where entities can have multiple parents and form complex interconnected graphs.
How it Organises Data
-
Uses nodes and set relationships
-
Supports many-to-many links
-
More flexible than the hierarchical model
Digital Support & Security Example
Modelling complex network topologies:
-
Devices connected to multiple switches
-
Firewalls linking multiple VLANs
-
Virtualised networks (SDN) with many connections
This helps technicians map out:
-
data flow paths
-
potential attack routes
-
dependency chains during troubleshooting
Strengths
-
Very flexible
-
Good for real-world networks
Weaknesses
-
Harder to design than relational models
Relational.
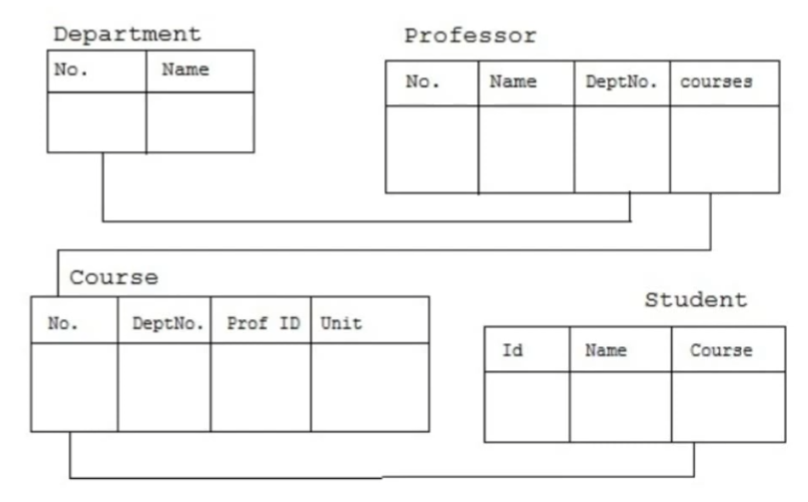
The most common model. It organises data into tables with rows and columns, linked by keys.
How it Organises Data
-
Data is stored in separate tables
-
Relationships use:
-
Primary keys
-
Foreign keys
-
-
SQL is used to query the data.
Digital Support & Security Example
A ticketing system database:
-
Users table → userID, name, email
-
Tickets table → ticketID, issueType, status, userID (foreign key)
-
Devices table → deviceID, OS, lastPatchDate
Security technicians use relational models to track:
-
failed logins
-
antivirus events
-
firewall logs
-
patch statuses
Strengths
-
Highly structured
-
Supports ACID compliance
-
Great for incident reporting
Weaknesses
-
Less effective for large unstructured security data
-
Requires normalisation and maintenance
“Choose and Justify the Data Model”
Duration: 20–30 minutes
Format: Individual or small group
Skills Developed:
- Understanding data models
- Applying theory to digital support & security contexts
- Justification and reasoning
- Technical communication
Scenario Overview
You have joined the Digital Support & Security team for a medium-sized organisation. Your manager wants to redesign several data systems to improve performance, security monitoring, and efficiency.
Each system uses a different type of data, and your job is to choose the most appropriate data model and justify your reasoning.
You must read each scenario, decide which data model fits best, and explain:
1. Why that model fits the system’s data and purpose
2. How it supports digital support or security tasks
3. What could go wrong if the wrong model is chosen
Use the data models below:
- Hierarchical
- Relational
- Network
-
Task Sections
Task A – Identify the Correct Data Model
Read each scenario and choose one data model.
Scenario 1 – Help Desk Ticketing System
The organisation wants a system to record:
- user details
- ticket categories
- timestamps
- ticket status (open/closed)
- technician assignment
The system must be able to run reports such as “tickets per department” and “average resolution time”.
Question:
What data model should this system use? Why?
Scenario 2 – Network Topology Mapping
You are building a tool that shows:
- switches linked to multiple devices
- firewalls with multiple inbound/outbound routes
- VLANs connected to different departments
- multiple links between nodes
Question:
Which data model can best represent these complex many-to-many connections?
Scenario 3 – SIEM Security Log Storage
Each security event generates information in JSON format, including:
- timestamp
- event type
- username
- IP address
- device
- geo-location
- risk score
Log volume is very high and changes every second.
Question:
Which data model can handle large volumes of semi-structured security log data?
Scenario 4 – Authentication Cache
Your system needs to store temporary information such as:
- active user sessions
- failed login counters
- account lockout timers
- IP-blacklist entries
These need to be retrieved very quickly.
Question:
Which data model is designed for fast lookups?
Scenario 5 – Cyber Attack Path Analysis
Security analysts want to visualise relationships between:
- users
- devices
- IP addresses
- events
- privileges
- lateral movement paths
They need to follow connections to find how a potential attacker could move inside the network.
Question:
Which data model is best for mapping connected relationships?
Scenario 6 – Company Directory (Active Directory Style)
You must store:
- organisation
- departments
- sub-groups
- users
- devices
Access policies need to be applied to whole branches (e.g., “all students”, “all admin staff”).
Question:
Which model fits a parent→child structure?
What is a SIEM?
Task B – Short Justification Table
Fill in a table like this:
+----------------------+---------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| | | |
| Scenario | Data Model Chosen | Justification (3-4 Sentences |
+----------------------+---------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| | | |
| 1 | Relartional | |
+----------------------+---------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| | | |
| 2 | Graph | |
+----------------------+---------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| | | |
| etc | | |
+----------------------+---------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
You must explain:
- why your choice fits the data
- how it supports digital support/security
- what limitations it might have
Task C – Reflection
Write a short paragraph answering:
Why is it important to choose the correct data model in Digital Support & Security environments?
Think about:
- data integrity
- security monitoring
- response times
- system performance
- compliance (e.g., GDPR)
Task D (Optional Extension)
Design a simple visual diagram of any two of your chosen models, showing how the data is structured.
Examples:
- Hierarchical tree (like Active Directory)
- Relational tables with keys
- Graph of users → devices → IPs
- JSON document example for a SIEM event
3.10.2 Know and understand the factors that impact the selection of data model for organising data:
• efficiency of accessing individual items of data
• efficiency of data storage
• level of complexity in implementation.
3.10.3 Understand the benefits and drawbacks of different data models and make judgements about the suitability of data models based on efficiency and complexity.
Exam Preparation
1. State one benefit of using a hierarchical data model to organise data.
(1 mark)
2. State one drawback of using a hierarchical data model to organise data.
(1 mark)
3. Explain one benefit of using a network data model for complex organisational data.
(2 marks)
4. Explain one drawback of using a network data model when supporting modern digital systems.
(2 marks)
5. Relational data models are widely used in digital support services. Explain one reason why relational data models are efficient for accessing individual items of data.
(2 marks)
6. Give one reason why a document-based (NoSQL) data model may be more suitable than a relational model for storing large volumes of unstructured support logs.
(1 mark)
7. Explain one drawback of using a document-based (NoSQL) model for data that requires strict consistency.
(2 marks)
8. A small IT support company stores customer details and tickets in a single large spreadsheet.
They are considering moving to a relational database or a document-based model.
Explain two ways a relational model would improve efficiency compared to the spreadsheet.
(4 marks)
9. A college stores learner records such as attendance, marks, course enrolments and disciplinary actions.
The data needs to be accessed by multiple teams (support, safeguarding, curriculum).
Explain with justification which data model would be most suitable and why.
(6 marks)
This should follow the AO2/AO3 style seen in long-form questions in Paper 2.
10. A cybersecurity operations team stores millions of log entries per day from firewalls, servers and IoT devices.
They must query the data quickly during incident response.
Discuss the suitability of using:
- a relational data model
- a wide-column NoSQL model for this purpose.
Your answer should include the benefits, drawbacks and a justified conclusion.
(9 marks)
This mirrors the Level-based mark scheme style used in extended questions.
3.10.4 Be able to draw and represent data models:
• hierarchical models with blocks, arrows and labels
• network models with blocks, arrows and labels
• relational models with tables, rows, columns and labels.
Drawing and Representing Data Models
Scenario
You have been asked to help a junior member of the IT Support Team understand how different data models organise and present information.
To support them, you will create three diagrams that show the same small dataset using hierarchical, network, and relational models.
The small dataset is:
Company Departments
IT, HR, Finance
Employees
Each employee belongs to a department
Some employees work on more than one project
Projects
Cyber Upgrade, Website Redesign, Staff Onboarding
Your task is to draw each model in the format suggested.
Task Instructions
1. Hierarchical Data Model (Tree Structure)
Goal: Draw a tree using blocks, arrows and labels to show parent, child relationships.
What your diagram must include
“Company” as the root node
Branches for Departments
Each department pointing to its Employees
A simple name label on every block (e.g., “IT Department”, “Employee: Sarah”)
Instructions
Draw a box at the top labelled Company.
Draw three boxes below: IT, HR, Finance.
Draw arrows downward from Company to each Department.
Add at least two employees under each department and link them with arrows.
Make sure all arrows point one way (top -bottom).
Checklist
- One parent per child
- No cross-links between departments
- All entities labelled clearly
2. Network Data Model (Many-to-Many Links)
Goal: Draw a network diagram showing how employees can belong to more than one project.
What your diagram must include
Blocks for Employees
Blocks for Projects
Arrows (or connecting lines) showing links
Clear labels on all blocks
Instructions
Draw three employee blocks (e.g., Sarah, Tom, Aisha).
Draw three project blocks (Cyber Upgrade, Website Redesign, Staff Onboarding).
Connect employees to the projects they work on.
Example: Sarah → Cyber Upgrade and Website Redesign
Tom → Website Redesign
Aisha → Staff Onboarding and Cyber Upgrade
Use arrows or lines to show many-to-many connections.
Checklist
- Employees can link to more than one project
- Projects can link to more than one employee
- No “top node”; it is a web of connections
3. Relational Data Model (Tables, Rows & Columns)
Goal: Create a set of tables that show how data is normalised and linked using keys.
What your diagram must include
A Departments table
An Employees table
A Projects table
A Link/Join table for Employee Project relationships
Column names, primary keys (PK) and foreign keys (FK)
|
DepartmentID (PK) |
DepartmentName |
|---|---|
|
1 |
IT |
|
2 |
HR |
|
3 |
Finance |
|
EmployeeID (PK) |
EmployeeName |
DepartmentID (FK) |
|---|---|---|
|
101 |
Sarah |
1 |
|
102 |
Tom |
1 |
|
103 |
Aisha |
3 |
|
ProjectID (PK) |
ProjectName |
|---|---|
|
P1 |
Cyber Upgrade |
|
P2 |
Website Redesign |
|
P3 |
Staff Onboarding |
|
EmployeeID (FK) |
ProjectID (FK) |
|---|---|
|
101 |
P1 |
|
101 |
P2 |
|
102 |
P2 |
|
103 |
P1 |
|
103 |
P3 |
Instructions
Create the following tables as diagrams:
Table 1 - Departments
Table 2 - Employees
Draw arrows showing: Employees.DepartmentID → Departments.DepartmentID
Table 3 - Projects
Table 4 - EmployeeProjects (Join Table)
Draw arrows from both FKs to their parent tables.
Checklist
- Each table has a primary key
- Foreign keys link tables
- No repeated groups of data
- Structure supports many-to-many relationships
Extension Challenge (Optional)
Choose one of the three models and answer:
“Explain one benefit and one drawback of this model in a real IT Support or Security context.”
Last Updated
2025-12-08 09:46:28
English and Maths
English
Maths
Stretch and Challenge
Stretch and Challenge
- Fast to implement
- Accessible by default
- No dependencies
Homework
Homework
Equality and Diversity Calendar
How to's
How 2's Coverage
Links to Learning Outcomes |
Links to Assessment criteria |
|
|---|---|---|
Files that support this week
Week 9→
Next 9Week 10→
Next 10Week 11→
Next 11←
Prev9