week 4
Purposes and uses of WebsitesPurpose
When creating, using and developing a website you must try to understand the purpose of them. In your course, you will be given a scenario or setting to which you must make a submission to. It is vital that you understand who the audience of the site is as this can, and will lead to either success or failure.
When creating a site for a client that you will get paid for, who is the audience?
Consider the fact that an explanation can be interpreted in many ways, however when planning to create a product, in our case a website, we need to demonstrate that we understand what we are doing and for whom. The best way for us to demonstrate this is by writing down what our understanding is of our project before we even start to think about designing it. It is therefore very important that this is documented from the beginning of our project.
User Requirements
Now that you understand some part of the purpose of the site and intended target audiences it is time to look at the user's requirements, this could be a list of elements that they would like to see in a website, it could also include the features that they would like to have too.
Examples of the types of requirements that a client could require would be things like;
- An area where new users could go to create an account to login
- A shopping cart to allow users to buy goods or services.
- A search bar so that they could quickly search for areas of interest.
The list above is only an example and not likely to be required in your assessments, however, this concept of a list should be identified and acknowledged when writing about the user's requirements in any document so that your client (your tutor) is aware that you know what you need to include in your site.
What type of language would you use in a portfolio website?
Word of the Day, use the QR code in the class to find out. Whats its Scrabble score?
What types of features would you expect to appeal to a target audience of web users that are close to your age? What features would you select to appeal to different genders? Why would different genders have different features? Would this affect the overall appearance of the site?
Design Documentation
The process of creating a website or the vision of a website begins at the design stage, you will have at this point been given the details of the users requirements and the target audience, with all of this detail now at your disposal you can produce your vision of the site through the use of, Storyboards, Timelines, Hierarchy diagrams, assets lists and a purposed test plan. These documents are a key piece of evidence that once created will provide a set of guidance documentation that will keep the final development of the site on track.
Let's look closer at these documents and their unique importance.
Storyboards
Close your eye's, and clear your mind, You are standing in a field, in front of you are some mountains, at the foot of these are some animals under a tree. Discuss as a group what your vision was.
Possibly one of the most key documents that have the ability to save time, a well-created storyboard can provide the detail and information to how a site should look and feel. The more detail the better, in the web development sector this stage can be done by a person that is in another country and the developer will be given these drawings and be expected to create the site from them.
create a storyboard of a website that you visit DO NOT INCLUDE THE TITLE/NAME OF THE SITE IN YOUR DESIGN, try to create this without loading it up on your screen, share this with another person in your class, see if they are able to tell you what site that they have chosen.
Now that you have swapped your storyboards with others in the group, identify the areas that they could have improved on thier storyboard to make it more clear as to the site that they choose.
Storyboards should be supported with some text to enable further understanding, such as the links to content or the overall intended feel and direction of the page.
The example below demonstrates the simplest version of a storyboard.

A further example of a detailed storyboard.
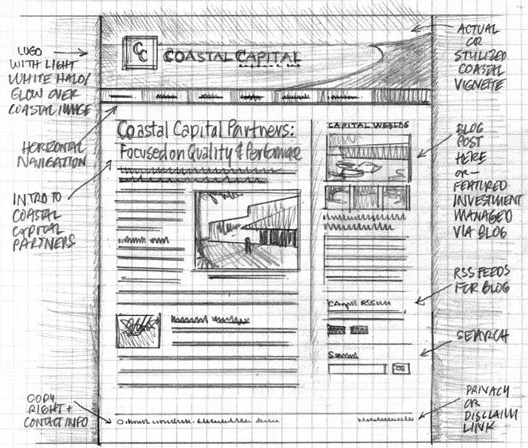
Some storyboards are taken further by creating a mockup, these are photoshop or image editor graphics that are constructed to make an example of how the web page may actually look on a web browser.
Assets List
The creation of a website may require you to include key images, links to videos or files, the logging of this is therefore important and vital. However at the beginning of the project, your client may already have some of these for you, this could be things like logos and examples of work. This needs to be logged and included in an asset table for a number of reasons.
- logging of the assets for promoting purposes, so when creating the site these can be used and gathered quickly.
- Listing premade assets that have been found that could be of use in the website, these may not appear in the final product, but it is still worth keeping a record of them.
So what should your assets table look like?
| Name of Asset | Type of Asset | Source | Location/Intended Placement | File Size | Copyright |
| Me.jpg | Image | My camera | Home page, about me | 1200Kb | No my image |
| BTEC Logo.png | Image | www.Pearsons.co.uk | Qualifications | 1Mb | Yes |
The examples in the table above demonstrate that you understand the name of the file, what kind of file type it is, where the file came from, your intentions with the file, the size of the file and finally whether the file is copyrighted so may need permission to use it.
File Types
File types that could be used are;
| Graphical File Formats | Moving File Formats | Audio File Formats |
|
.bmp |
mp4 | .wma |
| .jpg | .avi | .mp3 |
| .tif | .wmv | .mpeg |
| .gif | .mov |
File Sizes and Compression
Remember that each of the above file types has different purposes and benefits and you should consider when and where you will use them. Things that can affect users and websites are the sizes of the files, for example, a tif image is not a compressed file this means that it is likely to be large, which could affect the loading time of a web page. Whereas a jpg is a compressed file format and this would be a better option for a graphical file type to use for a web page.
Timelines
To have a plan is to be organised! So with almost all projects, it is key to set out a plan of action in how you intend on completing the project. Each project will have a set of tasks that may happen at set points in time, or, that may need to be completed by a set time.
Let's use an example of building a house. Can you put the roof on before the walls have been built? No! so we have a logical order that must be followed and this is the same with creating a website. We can set this out from the beginning, the below is an example of a simple timeline/plan.
| Task | Day1 | Day2 | Day3 | Day4 | Day5 | Day6 | Day7 | Day8 | Day9 | Day10 | Day11 | Day12 | Day13 |
Day14 |
| find assets | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| create storyboard | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| create an alternative design | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| create assets | x | x | ||||||||||||
| create program | x | |||||||||||||
| test program | x | x | ||||||||||||
| update program | x | x |
Create a timeline template, add to it a plan on how you will prepare for christmas, consider research time, shopping and setting up your christmas tree.
Hierarchy
The understanding of the flow of the pages is important, we can draw how we would like the pages to link to each other very simply, the image below outlines this.
Last Updated
2018-04-16 13:27:00
English and Maths
English
0
Maths
Stretch and Challenge
Stretch and Challenge
- Fast to implement
- Accessible by default
- No dependencies
Homework
Homework
Equality and Diversity Calendar
How to's
How 2's Coverage
Learning Capture - Teachers allocate time at the end of the session for the group to write down what they think they have learned. The information shared helps the teacher to see which content he may need to revisit and so shapes future planning.
Traffic Lights - Learners use green, amber and red traffic lights to indicate levels of understanding and to attract support from peers and the teacher.
0
Links to Learning Outcomes |
Links to Assessment criteria |
|
|---|---|---|
Files that support this week
Week 3→
Next 3Week 4→
Next 4Week 5→
Next 5←
Prev3