week 9
Learning Aims and Objectives:
Aim: In this week's page, students will learn .
Objectives:
1. By the end of this week's page students will be able to
2. By the end of the week's page students will be able to
3. By the end of the week's page students will be able to
4. By the end of the week's page students will be able to
5. By the end of the week's page students will be able to
World Wide Web

http://tw.rpi.edu/
The World Wide Web as we know it is credited to a single persons visions and commitment to enable people to have access to information in an easy linked way. Sir Tim Burners-Lee an Englishman created the core elements to enable the hosting and sharing of information using a number of protocols.
HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol
URL – Uniform Resource Locator
The platform that Burners-Lee provided enabled people to turn computers in to webservers to share the information that was on them to others using the correct software. The webserver stores the original file and then if a user requests to see this file a copy of it is sent to the user/client.
When we look in to webpages we can see that these pages are linked together via the use of Hyperlinks, these are a kind of string that allows some one to follow the string to another page. Websites are made up of a number of these links and some of them can be to webpages that have been created by other people.
As mentioned earlier, users/clients use special software in order to request these files and webpages, these are often referred to as Browsers. These programs interpret the information that is sent to them by the webserver and present the webpages in a form that we can recognise. The information that is sent by the webserver is the webpages code, this is known as HTML or HyperText Mark-up Language. This code is created by the user/owner of the webpage and uses Tags to create the pages. Theses HTML tags always start with a bracket < and then close with a bracket > and example of this is in the box below.
There a lots of HTML tags that are used to create a webpage below is a small example of a few of them It is worth noting that most HTML tags have what are known as closing tags as per the example below
a paragraph
URLS
As discussed earlier one of the protocols that is used in the use of Surfing the Web is the use of a URL, these are used to direct a user to the correct location of a website. Lets look a little deeper, an owner of a website will use a computer to Host the website that they have created, this computer will have an address, this address is known as an IP address (this has been covered earlier, week 8) this address like your home address is unique, however the address is a IP number which could be something like 210.68.187.250 this number has no meaning and could be easily forgotten, so we use a service called a DNS or Domain Name Service that links the IP addresses to a written address like http://www.MyStudentSite.co.uk.
An URL also has other information in it to help the client’s software known what to do and where to go, The HTTP://www.MyStudentSite.Co.Uk/Subjects/OnlineWorld1/index.html
HTTP:// part of the URL tells the browser that the Protocol will be for a webpage
www.MyStudentSite.co.uk tells the browser the Domain which is the name/address of the website
/Subjects/OnlineWorld1/index.html tells the browser the Path of a specific part of the webserver to gather information
Search Engines
Search engines are a great way to find information from across the web, the search engine acts like a form of yellow pages or Thompson Local.

http://s.hswstatic.com/gif/market-online-business-2.jpg
There are number of popular search engines that are available, these are Bing, Google, Ask however there are a number of alternatives to these popular engines, and also there are a number of engines that were popular however they fell out of favour.
ACTIVITY: create a time line of web browsers.
The search engine will take a word, sentence or phrase and look over its database of web pages and it will look for the keywords and then present the user a list of the possible matches that have been found based on the search. In order for the search engines to gather this data they have a few tools that is uses to gain these vital references. Search engines use of Crawlers to read the webpages content and create a list of common words and terms that occur on the page, these crawlers then return the information to the search engines database to be indexed like a library system. These crawlers are also known as Web spiders, Web crawlers and bots. These are all automated and have no human involvement. Other ways that websites can appear on search engines, and to be listed at the top of the page is by paying to search engine to list them on the top of the criteria when a user enters a Keyword. These are known as sponsored links.
Email – Purpose and Use
What is Email? Often referred to as Electronic mail, email is a digital letter sent to someone that may require information or may need to be aware of information that is being discussed and sent. Email systems have a number of points to which are important and essential to enable users to send the mail. When looking at the image above we can see that users have a number of inputs and buttons that can be used and are required to be used to send the message. Let’s look in to them with a little more focus.
To .. – This area is one of the required area that are used to identify whom the message is required to be sent to.
Cc .. - This area is used to enable users to add people/users to see the message, however the message may not directly affect them. An example of this would be a message sent to a child inviting them to a party but the mother of the child was Cc’d about it so that she knew that they had been invited. Cc stands for Carbon Copy.
The Send Button – This is used to send the message once the person has entered an address of the people that they wish it to go to.
The Paper Clip Button – This is used to enable the users to attach a file to the email.
Address Book – This is where the information of people’s addresses and other details are stored, this is similar to the traditional paper version of an address book.
Create an infographic that highlights and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of emails. Include the use of CC and BCC and the capabilities of Email.
High Priority – This button enables users to make the recipient/ receiver of the email aware that the contents are important, this could be something like a change of room for a lesson that is due after lunch.
Low Priority – This button enables users to make the recipient/ receiver of the email aware that the contents are of low importance, this could be something like a message wishing people a Happy Christmas.
The Flag – This is a button that allows the recipient to put a flag on an email that they have read to review or action something later.
Emails have a number of other features and tools that can be used and most are common across different email software.
When we use email we must consider a number of areas and be aware of potential disadvantages of using such a system. We know that we are able to send emails that have attachments to them, however these can spread viruses. We can send these emails to multiple people at once, this could open up more users to virus infections quickly It is faster that Post or Snail mail as it became to be known.
You can record information in to a contact book of people’s addresses so that you can respond to them when required. Lots of web company’s offer email accounts for users to create their own bespoke names, e.g. [email protected] and these can be accessed anywhere an internet connection exists. We know that emails can be intercepted and data stolen and or edited to enable users to get information for unsuspecting users. Some users in the real world send emails pretending to be someone or a company to try and get others to send personal information, this is called Phishing. Things to look for that identify spam emails are misselt words, requests for pin numbers, email address that are very strainge.
Those of us with email find that our email accounts are at times flooded with emails that have no relevance to us at all, this is called Spam.
IMAGE of Spam.
How Email works

http://www.successbydesigns.net/blog/wp-content/uploads/2010/05/imap_pop.jpg
An email account uses a number of different Protocols to send and receive emails, these are;
POP3 – Post Office Protocol 3 – This protocol Pulls the email from an email server to a client’s PC when requested
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol – This is used for Webmail
SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol – This protocol pushes the email from the mail server to the clients pc when a new mail arrives.
The email server will store the email on the server until the client is ready and requests the email.
Create poster of the different email types and make this clear enough for a non -IT-Literate person to understand. Give examples to support your explaination and make this a single page in dimensions. Include images and titles to make your poster stand out.
Data Exchange Packet Switching
The term packet switching refers to the process of data being broken in to parts called packets before it is sent over a network or the internet and then how it is reassembled when it gets to its destination. When we look at the packets each will have a section of the data contained within it, these are limited in their size. A packet will have the following information contained within it; Error Control Bits – This part of the packet checks to see if the packet has been assembled correctly.
Data (Payload) – The core data being sent.
Source Address – Where the data packet has comefrom.
Destination Address – Where the data packet is intended to go.
Packet Identification – This part of the packet identifies the packet type so that the system knows how to reassemble them.
The life of a packet
VOIP and Packet Switching
As we have covered in earlier sessions VOIP or Voice Over Internet Protocol is a great way to communicate over the internet. Because VIOP data is sent over the internet these data packet will need to go through packet switching, however there is a small additional step, VIOP makes use of a thing called CODEC, this term is created from the following two process that are done to the data.
COmpression - This reduces the size of the original data to smaller digital file sizes that are then in sizes to be broken in to packets that can be sent on
DECompression – This takes the packets data and decompress it back in to the form that can be presented to the user at the other end.
Why do we use packet switching, what are the benefits?
The use of breaking down the data in to packets means that the file if they were big would not clog up the network as parts of it can be sent a chunk at a time and then once the complete packet group arrives it will construct them back in to the correct order. Using packet switching allows for the users to have an added security element as if a packet is intercepted it only contains small parts of the data in it. There is a disadvantage to this method as if a packet is lost or corrupted during transmission the whole file will not be received correctly.
Data Exchange and Transmission Modes
We understand that almost everything that communicates will have a sender and a receiver, this is not only computers it could be phones, printers and remote controls. How these communicate are a little more detailed.
Full-Duplex - Consider a verbal conversation both people can talk at once, there are devices that can do this also, things like networks.

http://ecomputernotes.com/images/Full-Duplex-Mode.jpg
Half-Duplex – Consider a conversation or a question one device/person listens then the other reponds one they have all the information. The conversation can go both ways but cannot transmit at the same time

http://www.sqa.org.uk/e-learning/NetTechDC01BCD/images/pic012.jpg
Simplex – This is a one way conversation, this is common of TV remote controls.

http://ncsmindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/26.jpg
Discuss and find 2 examples for each of the transmission.
Characteristics of Data Transfer
http://helpingtutorial.blogspot.co.uk/2013/01/serial-communication.html
Serial – In a serial connection the information communicated across the connection is sent a bit at a time, this allows the information to be sent over large distances, however this infomation is broken in to parts to be communicated.
Parallel - In a parallel connection with a device data can be communicated simultaneously over a physical connection for example a printer cable. Because of the way that this can send information simultaneously the data is communicated faster, however a downside to this type of transmission is that the data can only travel over a small distance, the maximum recommended by most cable manufacturers is approximatly 5 meters.
Wired Transmission Methods
Let’s now look at what ways we can send information between devices using a physical method of connections.
Firstly we should review where we come in to contact with these connections!
During our day to day activities we watch TV and we use our computers. How do these devices receive their signals? Lets look closer.
Your computer connects to a network that communicates data packets around it to hopefully be received by the intended device, this information travels from your PC (when wired to the network) through an Ethernet cable also referred to as network cable. These cables are made up of a number of small cables in side of a plastic protective layer that wraps around it. Inside of these cables are 8 small strands
.png?width=200)
http://www.broadbandbuyer.co.uk/images/products/bbbuyer/rj-600(b).png?width=200
Ethernet Cables
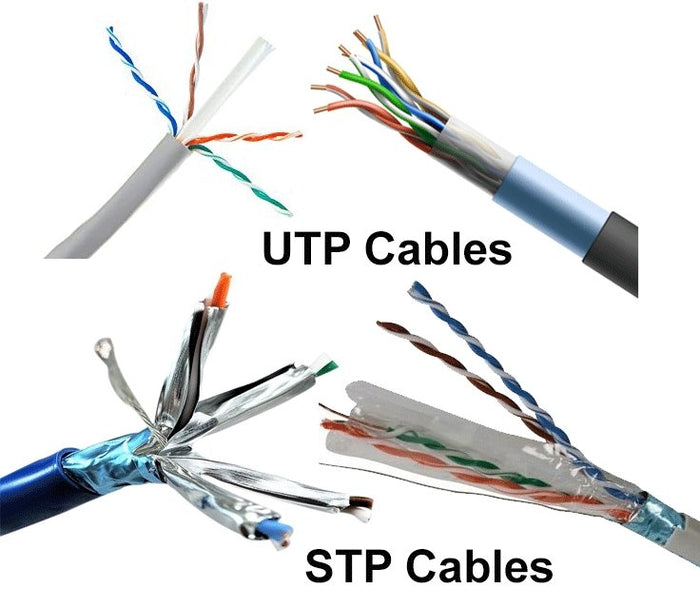
These cables can come in two different types these are UTP and STP these terms mean that the cable has additional features that the other has not.
UTP – Unshielded Twisted Pair, these cables are all twisted inside of the cable
STP – Shielded Twisted Pair, an additional layer of protection has been added to enable the cables data to be protected from interference.
This is commonly used in home computing because of the expense as these cables are cheap to create and cheap to buy and are reliable.
However it is worth remembering that these are not able to shield from digital noise which is when a cable is close to another digital device or signal.
Coaxial
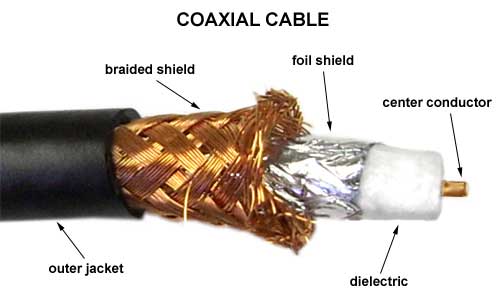
http://atx2000.altervista.org/Schemes/coax_cables/image001.jpg
This is commonly used in the connection of TV and aerials, they are very reliable in transferring the TV signals to the TV. This type of communication was previously used in computing before the use of Ethernet cables.
Fibre Optic

http://atx2000.altervista.org/Schemes/coax_cables/image001.jpg
This is by far the fastest connection that can be used to transfer information. Using light computers send this information down the cables a lightening speeds. This technology is very expensive however and very complicated to install. The cables are made from either glass or high quality plastic. Because the signals sent are light the information can be sent over long distances.These are commonly used in the connections of server on the Backbone of a network.
How its made
How it works
Wireless Transmission Methods

http://www.clker.com
Let’s now look at what ways we can send information between devices using a wireless method of connections.
Firstly we should review where we come in to contact with these connections!
During our day to day activities we use our mobile phone and our laptops. How do these devices receive their signals? Lets look closer.
Your computer connects to a network that communicates data packets around it to hopefully be received by the intended device, this information travels from your PC (when connect the network) through an wireless connection also known as WIFI.
WiFi is also known as Wireless Fidelity.
There are a number wireless methods to send information from device to device, these are,
Infrared

http://www.teach-ict.com/images/stk/remote_control_1.jpg
This form of wireless connection is not able to carry large amounts of information, and is limited in it range, normally this technology is used for things like remote controls for TV's, however early handheld PDA computers used this to send very small bits of data over a short distance, Like the TV remote these devices were required to be in line of sight for it to work.
Microwave

http://hotline.ccsinsight.com/_images-article/Bluetooth-Logo.jpg
This communication transmission uses shortwave to send information. It is one of the most commonly used short range communication methods, it is recognised as bluetooth.
Satalite

https://www.colourbox.com/preview/2966674-a-satellite-communication-concept-with-two-laptops-and-map.jpg
This is by best for connection, using satalites that are in orbit around the world data can be sent up and down quickly over large geographical areas.
Last Updated
2025-11-17 13:30:02
English and Maths
English
Maths
Stretch and Challenge
Stretch and Challenge
- Fast to implement
- Accessible by default
- No dependencies
Homework
Homework
Equality and Diversity Calendar
How to's
How 2's Coverage
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria.
Anonymous Assessment - Learners assess an anonymous piece of work containing deliberate mistakes against given success criteria.
Links to Learning Outcomes |
Links to Assessment criteria |
|
|---|---|---|
Files that support this week
Week 8→
Next 8Week 9→
Next 9Week 10→
Next 10←
Prev8